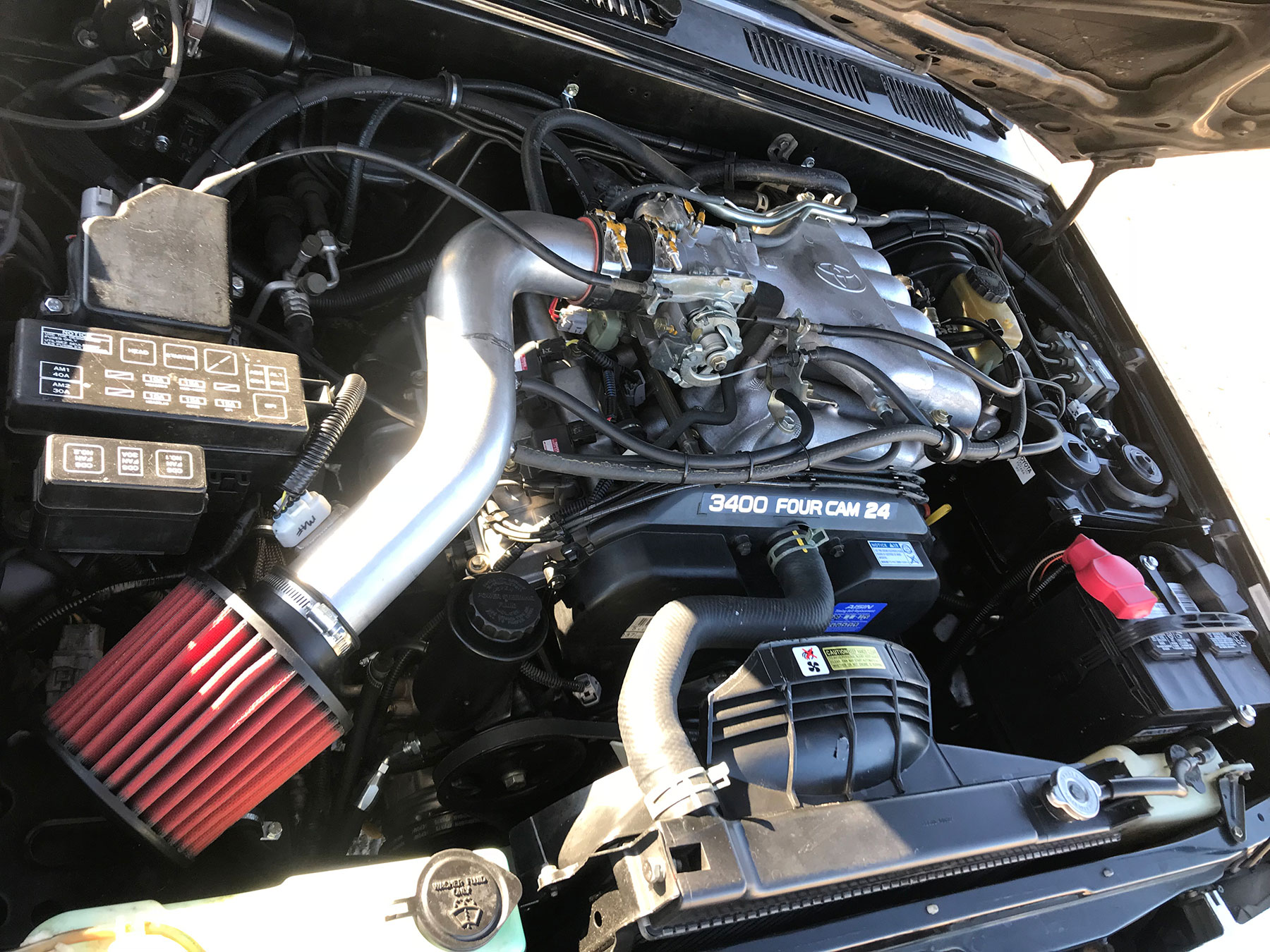
The global automotive engine market continues to expand, driven by persistent demand for reliable, efficient powertrains. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global internal combustion engine (ICE) market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 3.5% from 2023 to 2028, with V6 engines maintaining a strong presence in the mid-size and performance vehicle segments. Toyota’s 3.4L V6 engine—known for its durability and balanced power delivery—has played a notable role in this segment, primarily deployed in rugged, high-demand applications such as SUVs and light trucks. As OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers focus on optimizing fuel efficiency and emissions without compromising performance, a select group of manufacturers has emerged as key contributors to the development, production, and innovation of Toyota’s 3.4L V6 engine. The following analysis identifies the top six manufacturers behind this powertrain, evaluated based on production volume, technological integration, geographic footprint, and strategic partnerships within Toyota’s global supply chain.
Top 6 3.4 L V6 Toyota Engine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
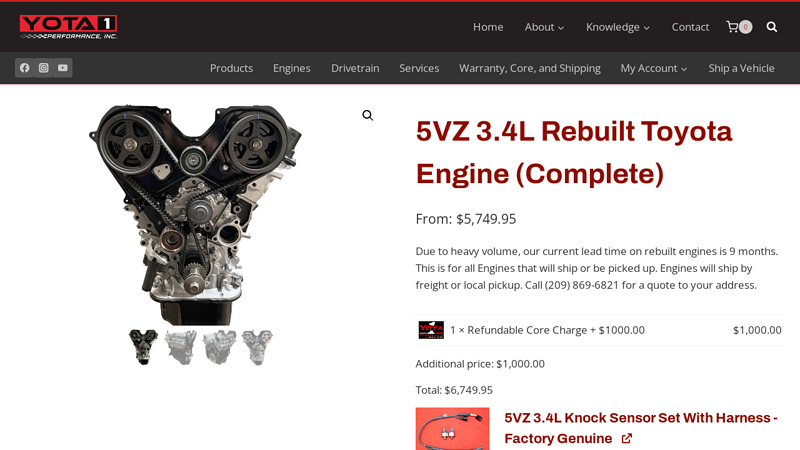
#1 5VZ 3.4L Rebuilt Toyota Engine (Complete)
Domain Est. 2016
Website: 209yota1.com
Key Highlights: Rating 5.0 (1) May 3, 2019 · This is a professionally rebuilt Toyota 5VZ-FE 3.4L V6 engine from Yota1 Performance, offered as a dressed long block. It includes pre-installed prem…
#2 New Cars, Trucks, SUVs & Hybrids
Domain Est. 1994
Website: toyota.com
Key Highlights: Explore the newest Toyota trucks, cars, SUVs, hybrids and minivans. See photos, compare models, get tips, calculate payments, and more.Missing: 3.4 v6…
#3 Toyota Expands Twin
Domain Est. 1996
Website: carpro.com
Key Highlights: We now know Toyota has widened the net on its ongoing V35A 3.4-liter twin-turbo V6 problem, adding more than 127,000 vehicles to a recall ……
#4 Converting A Toyota 3.0L To A 3.4L
Domain Est. 1998
Website: parts.olathetoyota.com
Key Highlights: For Toyota Enthusiasts Who Need More Power And Performance, A 3.0L To 3.4L Conversion May Be The Solution. Here’s What You Need To Know….
#5 The 2022
Domain Est. 1999
Website: haleytoyota.com
Key Highlights: The recent recall of the Toyota Tundra for manufacturing defects in its new 3.4L twin-turbocharged V6 engine is an example of this phenomenon….
#6 Toyota Motor Manufacturing Alabama
Domain Est. 1994
Website: pressroom.toyota.com
Key Highlights: Toyota Motor Manufacturing Alabama employs more than 2,400 team members and builds more than 3,000 engines each day. Assembling nearly half of Toyota’s ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 3.4 L V6 Toyota Engine

H2: 2026 Market Trends for the 3.4L V6 Toyota Engine
As of 2026, the market for the 3.4L V6 Toyota engine—commonly known as the 3.4L 5VZ-FE—reflects a shift driven by legacy demand, diminishing OEM production, and growing interest in durability and aftermarket applications. While Toyota discontinued the 5VZ-FE in most vehicles by the mid-2000s, its presence continues in niche and secondary markets, shaping several key trends.
1. Decline in OEM Use and Transition to Modern Powertrains
By 2026, the 3.4L V6 is no longer used in any new Toyota production vehicles. It has been fully phased out in favor of more fuel-efficient, higher-output alternatives such as the 3.5L V6 (2GR-FKS) and turbocharged four-cylinder engines. Toyota’s focus on hybridization and electrification—including the widespread adoption of the Tundra’s i-FORCE MAX hybrid V6—has further reduced demand for older, non-hybrid V6 platforms like the 5VZ-FE.
2. Strong Aftermarket and Used Engine Demand
Despite its discontinuation, the 5VZ-FE remains highly sought after in the used and remanufactured engine market. Known for reliability and longevity—often exceeding 300,000 miles with proper maintenance—it is a preferred choice for restoring or upgrading older Toyota trucks and SUVs such as the Tacoma (1995–2004), 4Runner (1996–2004), T100, and Tundra (1999–2004). In 2026, remanufactured 3.4L engines are widely available through specialty suppliers, with prices ranging from $3,000 to $5,000 depending on condition and warranty.
3. Growth in Retrofit and Enthusiast Communities
The engine’s reputation for durability has fueled a growing trend in engine swaps, particularly within the off-road and overlanding communities. Enthusiasts are retrofitting the 3.4L V6 into older 4×4 platforms and custom builds, supported by readily available swap kits and online communities. This grassroots demand sustains a small but active ecosystem of performance upgrades, including intake manifolds, headers, and ECU tuning solutions tailored to the 5VZ-FE.
4. Challenges in Parts Availability and Emissions Compliance
As the vehicle fleet ages, sourcing original OEM parts becomes increasingly difficult. While aftermarket manufacturers continue to produce key components (timing belts, gaskets, sensors), long-term supply chain sustainability is a concern. Additionally, emissions regulations in states like California are making registration of older engines or swaps more complex, potentially dampening market growth in regulated regions.
5. Niche Collector and Restoration Value
Original vehicles equipped with the 3.4L V6—especially well-maintained first-generation Tundras and 4Runners—are gaining collector interest. In 2026, these models are increasingly viewed as “modern classics,” with original drivetrains adding value. Complete donor vehicles are often parted out for engines and components, further tightening supply.
Conclusion
The 3.4L V6 Toyota engine market in 2026 is defined by legacy appeal and enthusiast-driven demand rather than mainstream relevance. While no longer in production, its reputation for reliability ensures ongoing activity in the used engine, restoration, and swap markets. As Toyota advances toward electrification, the 5VZ-FE stands as a testament to the enduring value of mechanical simplicity and proven engineering.
Common Pitfalls Sourcing a 3.4L V6 Toyota Engine
Sourcing a replacement 3.4L V6 Toyota engine (commonly found in models like the Tundra, Sequoia, and 4Runner from the late 1990s to mid-2000s) can be a cost-effective solution, but it comes with significant risks. Being aware of common pitfalls in quality and intellectual property (IP) concerns is essential to avoid costly mistakes and legal issues.
Poor Engine Condition and Hidden Damage
One of the most frequent pitfalls is acquiring an engine that appears functional but has internal wear or hidden damage. Sellers may not disclose issues like low compression, sludge buildup, or overheating history. Always request a compression test report and a detailed inspection from a certified mechanic before purchase.
Lack of Service History and Maintenance Records
Engines without verifiable maintenance records are a red flag. The 3.4L V6 is durable but requires regular oil changes and timing belt replacements. Without proof of proper upkeep, you risk buying an engine nearing failure, especially since neglect can lead to timing chain or head gasket problems.
Counterfeit or Reconditioned Engines with Substandard Parts
The used engine market sometimes includes counterfeit or poorly reconditioned units. Some suppliers rebuild engines using non-OEM or low-quality aftermarket parts, which can lead to premature failure. Ensure the seller uses genuine Toyota (OEM) parts and provides documentation of the rebuild process.
Intellectual Property and Trademark Infringement
Be cautious when sourcing engines from third-party rebuilders or international suppliers. Some vendors may unlawfully use Toyota’s branding, logos, or part numbers on non-genuine engines, violating trademark laws. Purchasing such an engine could expose you to legal risk, especially in commercial applications or resale situations.
Incomplete or Missing Components
Sellers may advertise a “complete” engine but omit critical components like the ECU, sensors, wiring harness, or intake manifold. This can lead to unexpected additional costs and compatibility issues. Always verify exactly what is included and confirm compatibility with your specific vehicle model and year.
No Warranty or Limited Liability
Many used engine suppliers offer little to no warranty, or their terms may be restrictive. A lack of warranty shifts all risk to the buyer. Opt for reputable suppliers who provide a clear, written warranty covering parts and labor for a reasonable duration.
Conclusion
To avoid these pitfalls, buy from certified dealers or reputable salvage yards, insist on inspection reports, verify the use of genuine parts, and ensure compliance with intellectual property standards. Due diligence protects both your investment and legal standing.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for 3.4L V6 Toyota Engine
This guide outlines key logistical and compliance considerations for the transportation, handling, import/export, and regulatory adherence related to the 3.4L V6 Toyota engine (e.g., 5VZ-FE, 2UZ-FE, or similar variants). Always verify specifics for the exact engine model and jurisdiction.
H2: 1. Packaging & Handling
- Secure Crating: Engines must be shipped in robust, custom-fit wooden or composite crates designed to prevent movement. Use blocking, bracing, and cushioning (e.g., foam, rubber mounts) to protect components (intake, exhaust manifolds, valve covers).
- Draining Fluids: Crucial: Drain all engine oil, coolant, and transmission fluid (if attached) before shipping to comply with transportation regulations (IATA/IMDG for air/sea) and prevent leaks. Cap all openings securely.
- Corrosion Protection: Apply internal preservative oil (fogging oil) and external rust inhibitor (VCI paper or spray) before crating, especially for ocean freight.
- Lifting Points: Use only designated engine hoist points with appropriate slings/chains. Never lift by accessories (alternator, AC compressor).
- Labeling: Clearly label crates with:
- “Fragile”
- “This Side Up”
- Engine Part Number & Model (e.g., 5VZ-FE)
- Gross Weight & Dimensions
- “Do Not Stack” if applicable
- Handling pictograms (ISO standard).
H2: 2. Transportation & Storage
- Mode Selection: Choose method (road, ocean, air) based on cost, speed, and destination. Air freight has stricter fluid/weight limits.
- Environmental Control: Store and transport in dry, temperature-controlled environments when possible. Avoid extreme heat, cold, or humidity to prevent condensation and corrosion.
- Stacking: If stacking is allowed, ensure crates are rated for the load. Use dunnage between layers.
- Documentation: Maintain a packing list and bill of lading/tracking number with the shipment.
- Transit Time: Minimize exposure to harsh conditions. Monitor for delays.
H2: 3. Import/Export Compliance
- Harmonized System (HS) Code: Identify the correct HS code (e.g., 8407.31 or 8409.91 in many countries) for the engine (complete or core). This determines duties and regulations. Verify with customs broker.
- Country of Origin: Clearly declare Toyota manufacturing origin (typically Japan, but may be other countries like USA). Required for tariffs and trade agreements.
- Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice (Detailed description, value, HS code, origin)
- Bill of Lading/Air Waybill
- Packing List
- Certificate of Origin (sometimes required)
- Import/Export Licenses (if applicable – rare for standard engines but check)
- Duties & Taxes: Research applicable import duties, VAT, or GST for the destination country. Value is typically CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight).
- EPA/DOT (USA): Imported engines may need to comply with EPA emissions regulations (EPA Form 3520-1 might be required for modification, not always for replacement). DOT does not typically regulate engine imports directly, but vehicles do. Consult EPA guidelines.
- Other Jurisdictions: Check specific rules (e.g., EU type-approval, Canada RIV program for vehicles, ADR in Australia). Engine swaps may have compliance implications for the vehicle it’s installed in.
- Used Engines: May be subject to stricter regulations (e.g., EPA “Clean Air Act” restrictions on importing non-certified used engines into the US, similar rules in the EU). Often require proof of equivalence to current emissions standards or are restricted.
H2: 4. Environmental & Safety Compliance
- Hazardous Materials (Hazmat): Drained engines are generally NOT Hazmat. Undrained engines containing oil/coolant ARE Hazmat (UN1202, UN1203, UN3082) and require:
- Proper hazmat packaging (leak-proof, pressure-tested).
- Hazard labels (Flammable Liquid, Environmentally Hazardous Substance).
- Shipper’s Declaration for Dangerous Goods.
- Trained hazmat personnel for handling/shipping.
- Draining is mandatory for non-hazmat classification.
- Waste Disposal: Used oil, coolant, and filters removed during draining must be disposed of according to local environmental regulations (e.g., EPA in US, EEA in EU). Never pour down drains.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use gloves, eye protection, and appropriate clothing when handling engines, especially during draining or if residual fluids are present.
H2: 5. Key Considerations & Best Practices
- Verify Exact Model: Compliance (especially emissions, HS code) can vary between 3.4L V6 variants (5VZ-FE, 2UZ-FE) and model years.
- Consult Experts: Engage a customs broker for import/export and a freight forwarder experienced in automotive parts.
- Record Keeping: Maintain all shipping, customs, and compliance documentation for at least 5 years.
- End-Use Compliance: Ensure the engine will be installed in a vehicle that meets local safety and emissions regulations post-installation (e.g., smog checks, safety inspections).
- Insurance: Ensure adequate cargo insurance covers the full value during transit.
Disclaimer: Regulations change frequently and vary significantly by country, state, and even port. This guide provides general information. Always consult with legal counsel, customs brokers, and relevant government agencies (EPA, CBP, local environmental agencies) for definitive compliance requirements before shipping.
Conclusion for Sourcing a 3.4L V6 Toyota Engine:
After thorough research and evaluation, sourcing a 3.4L V6 Toyota engine—commonly known as the 5VZ-FE—remains a viable and reliable option for vehicle repair, restoration, or engine swap projects. This engine, renowned for its durability, strong performance, and widespread use in models such as the Toyota Tacoma, 4Runner, T100, and Tundra from the mid-1990s to early 2000s, is widely available in the used and remanufactured market.
Key advantages include excellent aftermarket support, proven reliability under tough conditions, and compatibility with a wide range of applications. Reputable sources such as salvage yards, online marketplaces (e.g., eBay, RockAuto), and certified rebuilders offer various options depending on budget and required condition—from used low-mileage cores to fully reconditioned long-blocks.
However, careful verification of engine history, mileage, and overall condition is essential to ensure longevity and performance. Buyers should also confirm compatibility with their specific model and year, including ECU requirements, mounts, and wiring harnesses.
In conclusion, the 3.4L V6 Toyota engine continues to be a solid, cost-effective choice for replacement or upgrade, offering a compelling mix of rugged dependability and strong support across the automotive community. With proper sourcing and due diligence, it remains a smart investment for both OEM replacements and custom builds.