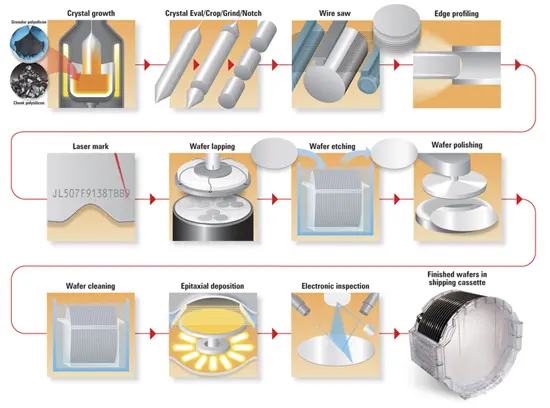
The global semiconductor industry is undergoing rapid expansion, driven by increasing demand for advanced electronics, electric vehicles, 5G infrastructure, and high-performance computing. Central to this growth is the 300mm wafer, which has become the industry standard for manufacturing cutting-edge integrated circuits due to its superior efficiency and scalability. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the semiconductor wafer market was valued at USD 13.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6.5% through 2029. This surge is fueled by the ongoing transition to smaller nanometer nodes and the rising adoption of 300mm wafers in front-end fabrication facilities. As capacity expansions continue across Asia-Pacific, North America, and Europe, a select group of manufacturers now dominate the 300mm wafer landscape, accounting for the majority of global supply. These top nine players are shaping the future of semiconductor production through strategic investments, technological innovation, and vertical integration. Below is an in-depth look at the leading 300mm wafer manufacturers driving this critical segment of the electronics ecosystem.
Top 9 300Mm Wafer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Siltronic / perfect silicon solutions
Domain Est. 1994
Website: siltronic.com
Key Highlights: Perfect Silicon Solutions: Positioned as one of the world’s leading manufacturers of silicon wafers with diameters up to 300 mm, Siltronic partners with many ……
#2 300mm Silicon Wafers
Domain Est. 1997
Website: wafernet.com
Key Highlights: WaferNet offers numerous standard 300mm silicon wafer options, also referred to as 12′′ silicon wafers, for our customer’s urgent needs….
#3 WaferPro
Domain Est. 2016
Website: waferpro.com
Key Highlights: WaferPro is a world leading silicon wafers supplier & manufacturer. We offer high quality silicon wafers, float zone silicon wafers, & SOI wafers in ……
#4 Company
Domain Est. 2020
Website: ferrotec-silicon.com
Key Highlights: Ferrotec Hangzhou Semiconductor Wafer Co., Ltd strives to be one of the world’s leading suppliers of semiconductor wafers….
#5 Sherman, Texas: 300mm wafer fabs
Domain Est. 1986
Website: ti.com
Key Highlights: Manufacturing in Sherman, Texas. Our 300-millimeter semiconductor wafer fabrication site in Sherman, Texas will manufacture millions of analog and embedded ……
#6 Manufacturing Services
Domain Est. 1995
Website: gf.com
Key Highlights: Wafer services · Bump offerings for 200mm and 300mm, including SnAg bump, copper pillar and WLCSP · Wafer sort with Known-Good-Die methodology · Backside grind, ……
#7 September 2025
Domain Est. 1996
Website: micross.com
Key Highlights: Foundries & Die Suppliers: Micross enables you to refocus product line resources to 300mm production by utilizing our world-class wafer processing and OSAT ……
#8 300mm Silicon Wafers
Domain Est. 1999
Website: universitywafer.com
Key Highlights: UniversityWafer, Inc’s silicon wafer manufacturing process can 300mm silicon wafers to very thin thicknesses both single and double side polished for all your ……
#9 Explore Our Range of High
Domain Est. 2017
Website: gw-semi.com
Key Highlights: GlobalWafers is a global leader in the manufacture and sale of wafers and related products to the semiconductor industry….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 300Mm Wafer

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 300mm Semiconductor Wafers
The global 300mm semiconductor wafer market is poised for significant evolution by 2026, driven by escalating demand for advanced electronics, continued process node scaling, and strategic industry investments. As the dominant platform for high-volume semiconductor manufacturing, 300mm wafers are at the center of technological and market transformations. Below are key trends expected to shape the 300mm wafer landscape in 2026:
-
Sustained Demand Growth from Advanced Nodes
By 2026, the transition to sub-5nm and 3nm process technologies—led by foundries such as TSMC, Samsung, and Intel—will continue to drive strong demand for 300mm wafers. These advanced nodes are essential for high-performance computing (HPC), artificial intelligence (AI) accelerators, and next-generation mobile processors. The high cost and complexity of developing and maintaining 300mm fabrication lines (fabs) favor only the most technologically advanced players, consolidating market leadership among key semiconductor manufacturers. -
Expansion of Fab Capacity Amid Geopolitical Rebalancing
Government initiatives such as the U.S. CHIPS and Science Act, the European Chips Act, and similar programs in Japan and India are spurring new 300mm fab constructions and expansions. By 2026, this will result in increased regional diversification of 300mm wafer production, reducing reliance on East Asian manufacturing hubs. Notable projects include Intel’s $20+ billion investments in Ohio and Arizona, TSMC’s Arizona fab, and Samsung’s Texas expansion. -
Strong Demand from Power Semiconductors and Analog Devices
Beyond logic and memory, 300mm wafers are increasingly used for power management ICs, RF components, and analog chips—segments benefiting from electric vehicle (EV) adoption, 5G infrastructure, and industrial automation. By 2026, more compound semiconductor and specialty analog manufacturers are expected to migrate to 300mm platforms to improve yield and reduce costs, further tightening supply-demand dynamics. -
Memory Market Recovery Fuels Wafer Consumption
The DRAM and NAND Flash markets, which are heavily dependent on 300mm wafers, are expected to rebound by 2026 following inventory corrections and renewed demand from data centers, AI servers, and consumer electronics. Major memory producers—Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron—are investing in EUV-enabled 300mm lines to enhance density and efficiency, increasing wafer utilization rates. -
Wafer Supply Constraints and Supplier Consolidation
The supply of 300mm wafers remains concentrated among a few global suppliers, including Shin-Etsu Chemical, SUMCO, SK Siltron, and GlobalWafers. Limited raw material availability (especially high-purity quartz and polysilicon) and long lead times for new production capacity may result in supply tightness through 2026. This is prompting longer-term supply agreements between wafer makers and foundries to ensure stability. -
Technological Advancements: SOI, Silicon Carbide on 300mm, and EUV Integration
Innovations such as Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) wafers on 300mm platforms and efforts to produce silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) epitaxial wafers on 300mm substrates are gaining traction. These technologies are critical for high-efficiency power devices and RF applications. Additionally, the widespread adoption of extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography on 300mm lines necessitates ultra-flat, defect-free wafers, pushing wafer manufacturers to enhance quality control and metrology. -
Sustainability and Cost Pressures
The environmental footprint of 300mm wafer manufacturing—particularly water and energy use—is under increasing scrutiny. By 2026, leading wafer producers are expected to implement more sustainable practices, including closed-loop water systems and renewable energy integration. Meanwhile, rising costs for equipment, materials, and skilled labor will pressure margins, prompting greater automation and yield optimization.
Conclusion:
By 2026, the 300mm wafer market will remain a critical enabler of global semiconductor innovation and supply chain resilience. Demand will be underpinned by AI, electrification, and digital infrastructure growth, while supply-side constraints and geopolitical factors will shape investment and capacity expansion. Companies that secure stable wafer supply, leverage advanced manufacturing techniques, and adapt to sustainability mandates will gain a competitive edge in the evolving semiconductor ecosystem.

H2: Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 300mm Wafers – Quality & IP Risks
Sourcing 300mm silicon wafers is critical for advanced semiconductor manufacturing, but it involves significant risks beyond simple procurement. Overlooking quality and intellectual property (IP) factors can lead to production delays, yield loss, legal disputes, and reputational damage. Here are the key pitfalls to avoid:
H3: Quality-Related Pitfalls
-
Inadequate Wafer Specification Alignment:
- Pitfall: Failing to precisely define and agree upon critical parameters (diameter, thickness, flatness (TIR/TTV), resistivity, oxygen/carbon content, crystal orientation, defect density (COPs, D-defects), surface roughness, particle count).
- Consequence: Wafers may be technically “in spec” but incompatible with your specific front-end process (lithography, epitaxy, implantation), leading to catastrophic yield loss or device performance issues. Different nodes (e.g., 7nm vs. 28nm) have vastly different requirements.
- Mitigation: Develop highly detailed, process-specific specifications co-signed by your process engineering and quality teams. Perform rigorous incoming inspection against these specs.
-
Insufficient Supplier Qualification & Auditing:
- Pitfall: Relying solely on supplier data sheets or past reputation without conducting thorough on-site audits of the wafer manufacturer’s fabrication facility (FAB), quality management system (ISO 9001, IATF 16949), and process controls.
- Consequence: Hidden process instability, contamination risks, or inadequate change control procedures can introduce undetected defects impacting your yield. Supplier financial instability could also disrupt supply.
- Mitigation: Conduct comprehensive technical and quality audits. Verify statistical process control (SPC) data, defect tracking systems, and raw material (polysilicon) traceability. Assess financial health.
-
Poor Lot Traceability & Contamination Control:
- Pitfall: Inadequate tracking of wafers from polysilicon ingot growth through slicing, lapping, etching, polishing, and packaging. Insufficient controls for metallic (Fe, Cu, Ni) and particulate contamination.
- Consequence: Difficulty in root-cause analysis for yield excursions. Cross-contamination can ruin entire batches of wafers in your fab. “Killer” particles or metals can create fatal device defects.
- Mitigation: Demand full lot traceability (from ingot to wafer lot). Verify supplier’s contamination control measures (cleanroom class, handling procedures, packaging – SMIF pods). Require regular contamination monitoring reports.
-
Inadequate Incoming Inspection & Sampling Plans:
- Pitfall: Relying solely on the supplier’s Certificate of Analysis (CoA) without implementing robust internal inspection protocols or using statistically invalid sampling plans.
- Consequence: Defective wafers slip into production, causing tool damage (e.g., cracked wafers in steppers) and yield loss. Late detection increases scrap costs significantly.
- Mitigation: Implement a risk-based incoming inspection plan using advanced metrology (AFM, optical inspection, four-point probe, FTIR, surface analysis). Use statistically sound sampling (e.g., AQL) based on criticality.
-
Unmanaged Process Change Notifications:
- Pitfall: Suppliers making changes to materials (e.g., polishing slurries), processes, or equipment without adequate notification or qualification lead time.
- Consequence: Sudden, unexplained shifts in wafer characteristics (e.g., surface roughness, defectivity) that your process isn’t qualified for, leading to yield crashes.
- Mitigation: Enforce strict contractual change control clauses (e.g., requiring 6-12 months notification for major changes). Establish a joint review process for any proposed changes.
H3: Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
-
Unclear IP Ownership & Licensing for Custom Wafers:
- Pitfall: Sourcing specialized wafers (e.g., SOI, strained silicon, custom resistivity profiles, epitaxial layers) without explicit contracts defining who owns the process IP developed during qualification or co-development.
- Consequence: Disputes over ownership of valuable process know-how. Supplier may use your developed processes for competitors. You may lose freedom to manufacture or switch suppliers.
- Mitigation: Negotiate clear IP clauses before development starts. Define ownership of background IP, foreground IP, and improvements. Specify licensing rights (exclusive, non-exclusive, royalty-free) for both parties.
-
Inadequate Protection of Your Process-Sensitive Requirements:
- Pitfall: Disclosing highly specific, performance-critical wafer requirements (beyond standard specs) without robust Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) and need-to-know limitations.
- Consequence: Revealing your technology roadmap, device performance targets, or unique process challenges to the supplier (and potentially their other customers), giving competitors insight.
- Mitigation: Use strong, specific NDAs. Share only the minimum necessary information. Consider using “black box” specifications where possible (e.g., “must pass test X” instead of “must have resistivity Y at depth Z”).
-
Supplier Access to Your Production Data:
- Pitfall: Granting suppliers access to your detailed yield data or defect maps for troubleshooting without strict data governance.
- Consequence: Supplier gains insights into your fab’s process capabilities, yield drivers, and potential weaknesses, which could be used competitively or shared.
- Mitigation: Limit data sharing to aggregated, anonymized data necessary for root cause analysis. Define strict data usage and confidentiality obligations in contracts. Use secure data transfer methods.
-
Failure to Audit IP Compliance:
- Pitfall: Assuming the supplier isn’t infringing third-party IP (e.g., patents on crystal growth methods, polishing techniques, metrology equipment).
- Consequence: Your use of the wafers could expose your company to patent infringement lawsuits from third parties, even if the supplier is the direct infringer. Legal and financial liability.
- Mitigation: Include IP warranty and indemnification clauses in the supply contract. Require the supplier to certify freedom to operate. Consider periodic IP diligence.
-
Overlooking Export Control & Geopolitical IP Risks:
- Pitfall: Sourcing wafers from regions with different IP protection standards or from suppliers potentially subject to foreign government influence, especially for advanced nodes.
- Consequence: Risk of IP theft, forced technology transfer, or supply chain disruption due to sanctions. Compromised security for sensitive applications.
- Mitigation: Conduct thorough geopolitical risk assessments. Prioritize suppliers in jurisdictions with strong IP protection and stable trade relationships. Include export control compliance requirements in contracts.
Key Takeaway: Sourcing 300mm wafers requires a strategic partnership mindset, not just transactional procurement. Proactive, detailed management of both quality specifications/processes and rigorous IP protection through robust contracts, audits, and clear governance is essential to mitigate these significant risks and ensure a reliable, secure supply chain for advanced semiconductor manufacturing.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 300mm Wafers
Overview
The transportation and handling of 300mm semiconductor wafers require stringent logistics and compliance protocols due to their high value, sensitivity to environmental conditions, and the highly regulated nature of the semiconductor industry. This guide outlines best practices, regulatory considerations, packaging requirements, and compliance standards essential for the secure and efficient movement of 300mm wafers across global supply chains.
Packaging & Handling Requirements
1. Protective Packaging
- FOUPs (Front Opening Unified Pods): 300mm wafers must be transported in standardized 300mm FOUPs compliant with SEMI E47.1 specifications. These pods protect wafers from particulate contamination and mechanical damage.
- Material: FOUPs should be constructed from electrostatic-dissipative (ESD) materials to prevent static discharge.
- Sealing: Lids must be hermetically sealed to maintain cleanroom-level particle control (ISO Class 1–5).
- Labeling: FOUPs must be clearly labeled with wafer type, lot number, date, and handling instructions (e.g., “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” “ESD Sensitive”).
2. Secondary Packaging
- Carriers & Cassettes: FOUPs should be placed in shock-absorbent carriers or transit containers designed for semiconductor transport.
- Cushioning: Use anti-vibration foam, gel pads, or air-ride suspension systems to minimize mechanical shock and vibration.
- Temperature-Controlled Crates: For long-distance or extreme climate transport, use insulated or active temperature-controlled shipping containers.
Environmental Controls
1. Temperature
- Maintain ambient temperature between 18°C and 25°C (64°F–77°F) during transit.
- Avoid thermal cycling; sudden temperature changes may cause condensation and wafer stress.
- Use data loggers to record temperature history throughout the shipment.
2. Humidity
- Relative humidity should be kept within 30% to 60% RH to prevent moisture absorption and metal corrosion.
- Desiccants may be used inside sealed containers if passive control is required.
3. Cleanroom Compatibility
- All packaging and handling must preserve ISO Class 1–5 cleanliness.
- Transportation containers should be cleanroom-compatible and particle-tested.
Transportation Protocols
1. Modes of Transport
- Air Freight: Preferred for high-value, time-sensitive shipments. Use dedicated cargo aircraft or secure passenger aircraft holds.
- Ground Transport: Use clean, climate-controlled, and shock-monitored vehicles.
- Sea Freight: Only recommended for non-critical, high-volume transfers; requires enhanced environmental sealing and monitoring.
2. Shock & Vibration Monitoring
- Integrate trip data loggers or IoT sensors to monitor:
- G-force impacts (>1G threshold alerts)
- Vibration frequency
- Tilt and orientation
- Data must be reviewed upon arrival to verify integrity.
3. Transit Time & Routing
- Minimize handling touchpoints.
- Prefer direct routes with minimal transshipments.
- Plan shipments to avoid extreme weather conditions or high-risk regions.
Regulatory & Compliance Standards
1. International Regulations
- ITAR/EAR (U.S. Department of Commerce): Some 300mm wafers (especially those used in advanced logic or memory) may be subject to export controls under the Export Administration Regulations (EAR), particularly if tied to restricted end-uses or destinations (e.g., China, Russia, Iran).
- Customs Compliance: Accurate HS codes (e.g., 8486.20 for semiconductor manufacturing equipment parts) and proper documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin) are required.
- REACH & RoHS (EU): Ensure wafers and packaging materials comply with substance restrictions.
2. Industry Standards
- SEMI Standards:
- SEMI E47.1: FOUP mechanical interface
- SEMI E62: Wafer map formats
- SEMI E152: Carrier identification
- ISO 9001 & ISO 14001: Quality and environmental management systems should be in place for all logistics providers.
3. ESD & Safety Compliance
- Compliance with ANSI/ESD S20.20 or IEC 61340-5-1 for electrostatic control.
- Personnel handling must be ESD-certified and wear appropriate garments in designated areas.
Security & Chain of Custody
1. Access Control
- Limit access to authorized personnel only.
- Use tamper-evident seals on containers and FOUPs.
- Implement RFID or barcode tracking for real-time visibility.
2. Tracking & Visibility
- Use integrated supply chain platforms (e.g., SAP, Oracle SCM) for end-to-end traceability.
- Provide real-time GPS and condition monitoring to stakeholders.
3. Anti-Theft & Fraud Prevention
- Shipments should be insured for full replacement value.
- Use secure logistics providers with semiconductor-specific expertise.
- Perform audits of logistics partners annually.
Documentation & Recordkeeping
- Maintain records of:
- Shipment manifests
- Environmental logs (temperature, humidity, shock)
- Customs declarations
- Compliance certifications (REACH, RoHS, ESD)
- Chain of custody forms
- Retain records for a minimum of 5 years for audit and compliance purposes.
Emergency Procedures
- Damage Protocol: In case of container breach or environmental deviation:
- Quarantine shipment immediately.
- Notify quality and engineering teams.
- Perform particle and electrical testing before wafer processing.
- Contamination Response: If exposure to uncontrolled environments occurs, wafers may require re-cleaning or rejection based on risk assessment.
Conclusion
Proper logistics and compliance for 300mm wafers are critical to maintaining yield, minimizing risk, and ensuring regulatory adherence. Adherence to SEMI standards, environmental controls, secure packaging, and export regulations ensures that wafers arrive at their destination in optimal condition. Partnering with certified logistics providers and investing in real-time monitoring technology enhances supply chain resilience and traceability across global operations.
Conclusion on Sourcing 300mm Wafers:
Sourcing 300mm wafers is a strategic imperative for semiconductor manufacturers aiming to remain competitive in today’s advanced technology landscape. The larger diameter offers significant advantages, including higher die per wafer yields, reduced manufacturing costs per chip, and improved processing efficiency—making it the industry standard for high-volume production of advanced nodes. However, sourcing 300mm wafers requires careful consideration of supplier reliability, material quality (e.g., silicon purity, crystal orientation), lead times, and long-term supply chain resilience.
Currently, the global supply is dominated by a few key wafer suppliers, creating potential risks related to supply constraints and price volatility. Geopolitical factors and increasing demand from AI, automotive, and IoT sectors further strain availability. Therefore, securing long-term supply agreements, diversifying suppliers, and investing in strategic inventory planning are essential to mitigate disruption risks.
In conclusion, while 300mm wafers offer clear economic and technological benefits, successful sourcing depends on building strong partnerships with qualified suppliers, ensuring rigorous quality control, and maintaining flexibility to adapt to market dynamics. Companies that proactively manage their 300mm wafer sourcing strategy will be better positioned to support scalable, cost-effective, and reliable semiconductor production.