The global market for electrical connectors, including 240-volt plug types, is experiencing steady expansion driven by rising demand in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. According to Grand View Research, the global electrical connectors market size was valued at USD 89.4 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.7% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing electrification, infrastructure development, and the proliferation of high-power appliances and electric vehicle (EV) charging stations—all of which rely heavily on robust 240-volt plug systems. Additionally, Mordor Intelligence forecasts continued momentum in the electrical plugs and sockets market, citing regional industrialization and stricter safety standards as key drivers. As demand surges, manufacturers specializing in 240-volt plug types are scaling innovation in durability, efficiency, and compliance. Below are eight leading manufacturers at the forefront of this evolving landscape.
Top 8 240 Volt Plug Types Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Meltric
Domain Est. 1997
Website: meltric.com
Key Highlights: MELTRIC offers a full line of industrial plugs and receptacles, including our signature brand of UL-listed Switch-Rated devices with DECONTACTOR™ ……
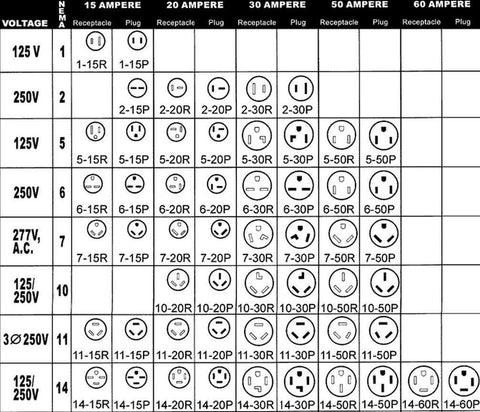
#2 NEMA Locking Reference Chart
Domain Est. 1996
Website: stayonline.com
Key Highlights: This NEMA receptacle chart provides technical drawings and specifications for NEMA locking plugs, receptacles, inlets, outlets, connectors and cords….
#3 NEMA Straight Blade Plug & Receptacle (Outlet) Configurations …
Domain Est. 1997
Website: elliottelectric.com
Key Highlights: The following tables show the straight blade plugs and receptacles for NEMA 5, NEMA 6, NEMA 7, NEMA 10, NEMA 14, NEMA 15, NEMA 18, and NEMA TT devices….
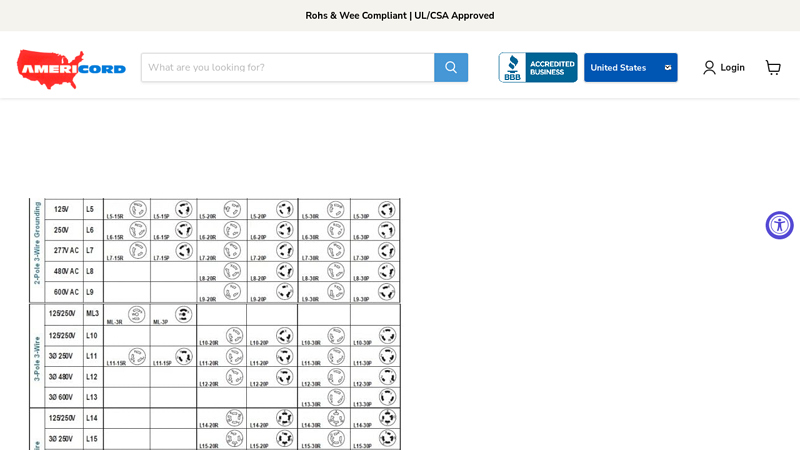
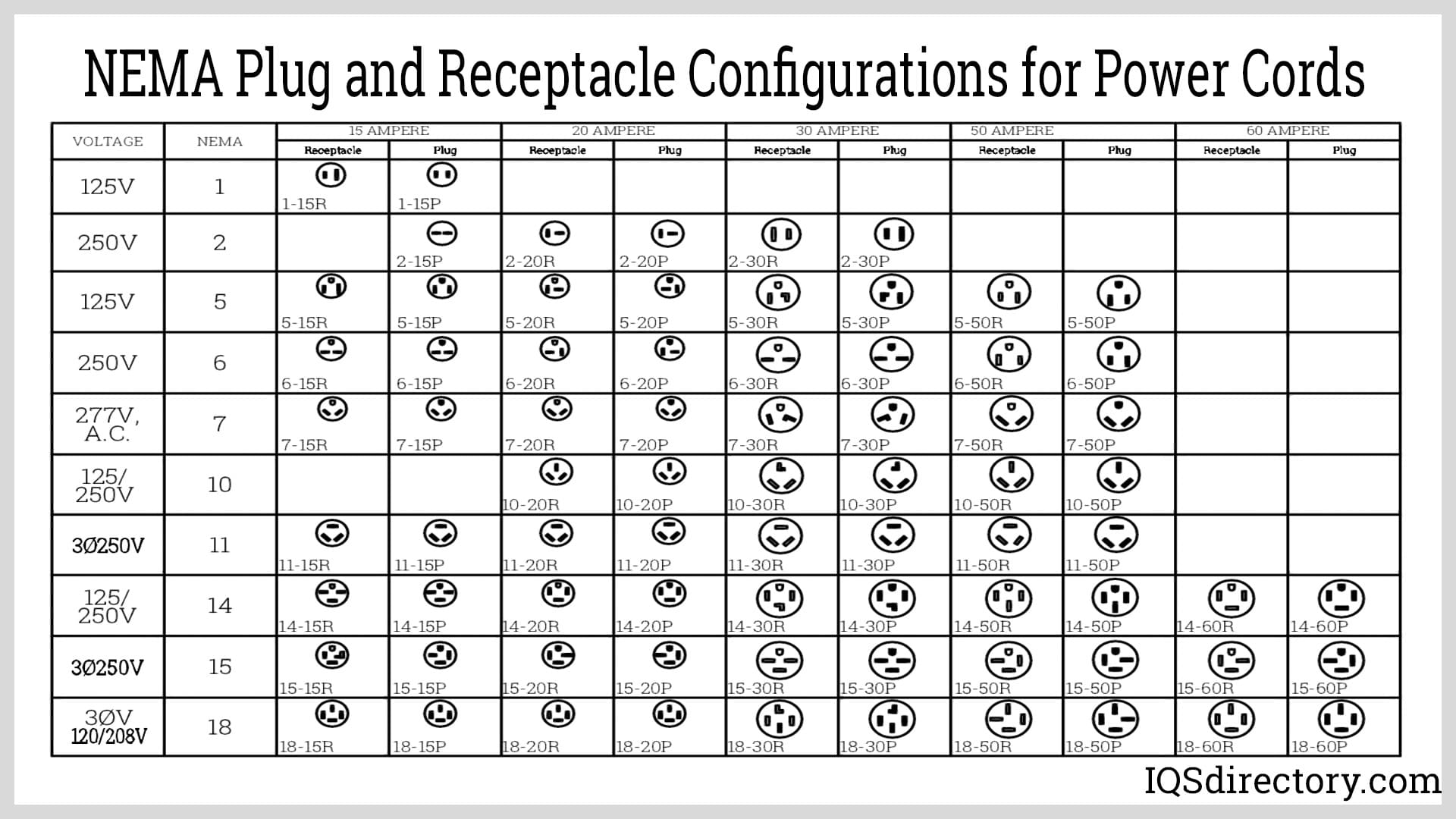
#4 NEMA Plug Charts
Domain Est. 1999
Website: americord.com
Key Highlights: These charts describe the layout of the connector plugs and sockets, voltage, and current limits, for their aim is to offer a uniform means of connecting ……
#5 North American Voltage Ranges
Domain Est. 2000
Website: quick220.com
Key Highlights: 220, 230, 240, and 250 volts are used to describe the higher 240 volt level. This higher voltage range supplies larger appliances such as clothes dryers, large ……
#6 NEMA Chart
Domain Est. 2010
Website: acupwr.com
Key Highlights: ACUPWR’s NEMA chart can help you identify which NEMA plug or receptacle you have. These plugs are used throughout the US, Canada, and Mexico….
#7 World plugs
Website: iec.ch
Key Highlights: The Type C electrical plug (or Europlug) is a two-wire plug that has two round pins. It fits into any socket that accepts 4.0 – 4.8 mm round contacts on 19 mm ……
#8 Types of Electrical Plugs
Domain Est. 2004
Website: iqsdirectory.com
Key Highlights: Explore the many uses and types of electrical plugs. Learn about plug adapters, replacement plugs, two-pronged and three-pronged plugs….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 240 Volt Plug Types
H2: 2026 Market Trends for 240-Volt Plug Types
As global electrification accelerates and energy demands evolve, the market for 240-volt plug types is poised for significant transformation by 2026. Driven by the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), home energy systems, and industrial automation, several key trends are shaping the adoption, standardization, and innovation in 240V connectors.
-
Expansion of Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure
The most influential driver for 240-volt plug adoption is the global EV boom. Level 2 EV chargers, which operate at 240 volts, are becoming standard in residential, commercial, and public charging stations. By 2026, demand for Type 1 (J1772) and Type 2 (Mennekes) connectors is expected to grow significantly—especially in North America and Europe, respectively. The European Union’s mandate for standardized Type 2 chargers across member states will reinforce this trend, while North America continues to rely on J1772 with increasing dual-capability installations. -
Regional Standardization and Harmonization Efforts
Regional differences in 240V plug types (e.g., NEMA 6-20, 6-30, 14-30 in North America; IEC 60309, Schuko in Europe; AS/NZS 3112 in Australia) remain a challenge. However, by 2026, industry and regulatory efforts are promoting greater harmonization—particularly in multinational EV charging networks and industrial equipment. Global manufacturers are increasingly adopting modular or multi-standard connectors to support cross-border compatibility. -
Growth in Residential and Commercial Electrification
The shift from fossil fuels to electric appliances (e.g., heat pumps, induction cooktops, electric dryers, and tankless water heaters) is increasing the need for reliable 240V outlets in homes and businesses. This trend is supported by government incentives for energy efficiency, particularly in the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and EU Green Deal. As a result, demand for NEMA 14-50 and similar high-amperage residential outlets is growing, especially in new construction and retrofits. -
Smart and Connected Plug Technologies
By 2026, “smart” 240-volt plugs with integrated monitoring, load balancing, and remote control capabilities will gain market share. These intelligent connectors, often used with EVs and home energy management systems, allow users to optimize energy usage during off-peak hours. Wi-Fi and cellular-enabled 240V outlets are becoming common in smart home ecosystems, enhancing energy efficiency and grid stability. -
Industrial and Data Center Applications
In industrial settings and data centers, 240V power delivery improves energy efficiency and reduces transmission losses. Three-phase 240V (or 400V line-to-line) systems using IEC 60309 connectors are increasingly deployed for high-power machinery and server racks. The trend toward higher-density computing and edge data centers will further boost demand for robust, standardized 240V plug solutions. -
Sustainability and Material Innovation
Environmental concerns are driving innovation in plug materials and lifecycle management. By 2026, manufacturers are expected to adopt more recyclable, flame-retardant, and heat-resistant materials. Additionally, longer product lifespans and modular designs will reduce electronic waste and support circular economy principles. -
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
With higher voltage comes greater risk, prompting tighter regulations. By 2026, expect stricter safety standards around grounding, arc-fault detection, and child-resistant designs in 240V outlets. Certification bodies like UL, CE, and IEC will play a growing role in ensuring compliance, especially in consumer-facing applications.
Conclusion
The 240-volt plug market in 2026 will be defined by technological innovation, regional standardization, and integration with smart energy systems. While regional plug types will persist, interoperability and intelligence will be key differentiators. Stakeholders—from manufacturers to utilities—must adapt to these trends to meet rising demand driven by electrification, sustainability, and digitalization.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 240 Volt Plug Types (Quality, IP Rating)
Sourcing 240-volt plug types requires careful attention to both quality and Ingress Protection (IP) ratings to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance. Overlooking key factors can lead to equipment damage, safety hazards, or project delays. Below are common pitfalls to avoid:
Poor Quality Materials and Construction
One of the most frequent issues when sourcing 240V plugs is selecting products made from substandard materials. Low-cost plugs may use inferior plastics that degrade under heat or UV exposure and conductive components with inadequate resistance, increasing the risk of overheating or short circuits. Always verify that plugs are manufactured from high-temperature resistant thermoplastics (e.g., polycarbonate or nylon) and feature copper or brass contacts with proper plating (e.g., tin or nickel) to resist corrosion and maintain conductivity.
Inadequate or Misrepresented IP Ratings
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating indicates a plug’s resistance to dust and moisture. A common mistake is assuming an IP rating without verifying its authenticity. Some suppliers may claim high IP ratings (e.g., IP67 or IP68) without third-party certification. Always request test reports or certifications from accredited bodies (e.g., IEC, UL) to confirm that the plug meets the stated IP standard under real-world conditions.
Non-Compliance with Regional Standards
240V plug types vary globally (e.g., AS/NZS 3112 in Australia, BS 1363 in the UK, NEMA 6-15 in North America). Sourcing the wrong type due to regional mismatch can result in incompatibility or code violations. Ensure the selected plug conforms to local electrical standards and is certified by relevant authorities (e.g., CE, UKCA, RCM, or CSA).
Insufficient Current and Temperature Ratings
Plugs rated below the actual load requirements can overheat and fail. For 240V applications, ensure the plug is rated for the correct amperage (e.g., 10A, 15A, 20A) and operating temperature. Using a plug with a marginal rating in high-demand environments (e.g., industrial machinery or EV chargers) increases fire risk.
Lack of Strain Relief and Durability
In industrial or outdoor settings, cables are subject to frequent movement and stress. Plugs without effective strain relief mechanisms may suffer internal wire breakage or loosening over time. Choose plugs with integrated cable clamps or overmolded designs that secure the cable and prevent tugging from damaging internal connections.
Counterfeit or Unbranded Products
Unbranded or counterfeit plugs often mimic reputable brands but lack safety testing and quality control. These products may pass visual inspection but fail under load or in harsh environments. Source from authorized distributors or directly from established manufacturers with verifiable product traceability.
Ignoring Environmental Conditions
Failing to match the plug’s IP rating and housing material to the environment is a critical oversight. For example, using an IP44-rated plug in a washdown area (requiring IP66 or higher) can lead to water ingress and electrical faults. Assess the operating environment—indoor, outdoor, dusty, wet, or chemically exposed—and select accordingly.
Poor Terminal Design and Installation Issues
Inferior terminal blocks can lead to loose connections, arcing, and overheating. Look for plugs with screw-type or spring-clamp terminals that ensure a secure, low-resistance connection. Poor terminal access or design can also complicate field installation and increase the risk of errors.
By avoiding these common pitfalls—prioritizing certified quality, accurate IP ratings, regulatory compliance, and environmental suitability—buyers can ensure safe, long-lasting performance of 240-volt plug systems.
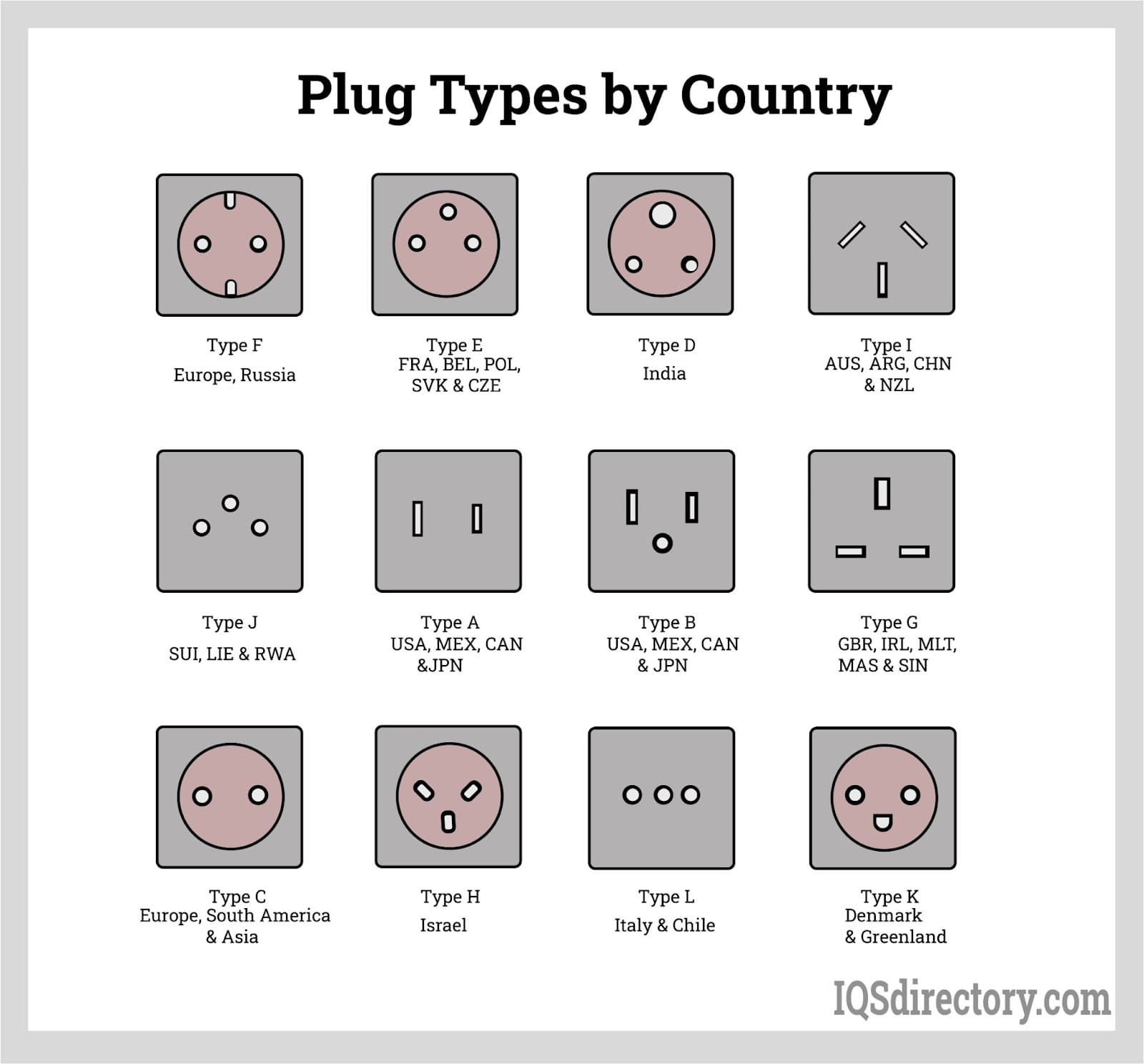
Logistics & Compliance Guide for 240 Volt Plug Types
Understanding 240 Volt Electrical Systems
240-volt electrical systems are commonly used for high-power appliances such as electric dryers, ovens, air conditioners, and industrial equipment. Unlike standard 120-volt outlets, 240-volt systems deliver power through two live wires (typically carrying 120 volts each, out of phase) and often include a neutral and ground wire. The plug and receptacle types vary significantly by region and application, making compliance and logistics critical for international shipping and installation.
Common 240 Volt Plug Types by Region
Different countries and regions utilize standardized plug types for 240-volt applications. Selecting the correct plug ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
North America (NEMA Standards)
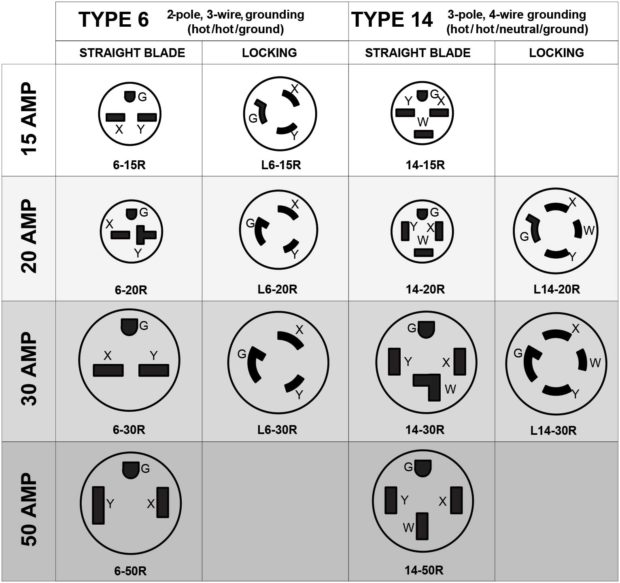
– NEMA 6-15P / 6-15R: 240V, 15A, two hot wires and ground (no neutral); used for air conditioners and shop tools.
– NEMA 6-20P / 6-20R: 240V, 20A; similar to 6-15 but with a horizontal neutral slot for higher amperage.
– NEMA 10-30P / 10-30R: Older dryer outlet (240V, 30A, two hots + neutral, no ground); being phased out.
– NEMA 14-30P / 14-30R: Modern dryer plug (240V, 30A, two hots + neutral + ground); widely used.
– NEMA 14-50P / 14-50R: 240V, 50A; common for electric ranges, RVs, and EV chargers.
Europe (IEC & CEE Standards)
– CEE 7/4 (Schuko, Type F): 230V, up to 16A; commonly used in Germany, France, and neighboring countries.
– CEE 7/7 (Hybrid Schuko/French): Compatible with both Type E and F sockets; 230V, 16A.
– IEC 60309 (Industrial Plugs): Color-coded (red for 230V/400V); available in 16A, 32A, 63A variants; used in commercial and industrial settings.
Australia & New Zealand (AS/NZS 3112)
– AS/NZS 3112 (Type I): Standard 240V plug; 10A or 15A ratings; slanted pins with earth connection.
– High-current variants: Used for air conditioners and electric water heaters; often 32A or 63A IEC 60309 connectors.
United Kingdom (BS 1363 & BS 546)
– BS 1363 (Type G): Standard 230V domestic plug; fused, 13A; not typically used for high-power appliances.
– BS 546 (Legacy): Older 15A, 30A, or 60A round-pin plugs; still found in some industrial applications.
Logistics Considerations for International Shipments
Shipping equipment with 240-volt plugs requires careful planning to ensure compatibility and compliance.
Voltage and Frequency Verification
– Confirm local voltage (e.g., 230V in EU, 240V in AU) and frequency (50Hz vs 60Hz).
– Mismatches can damage motors and electronics.
Plug Adapters vs. Hardwiring
– Avoid relying solely on plug adapters for high-power devices; they may not meet safety standards.
– Consider hardwiring equipment or supplying region-specific plugs during manufacturing.
Labeling and Documentation
– Clearly label voltage, frequency, and plug type on equipment and packaging.
– Include multilingual installation guides with compliance markings (CE, UKCA, RCM, etc.).
Customs and Import Regulations
– Verify that plug type and equipment meet local safety standards (e.g., UL in USA, CE in EU, RCM in Australia).
– Provide certification documentation (e.g., test reports, conformity certificates) to avoid customs delays.
Compliance and Safety Standards
Adhering to electrical safety standards is mandatory for market access and user protection.
North America
– Equipment must comply with UL 498 (plugs and receptacles) and NEC (NFPA 70) for installation.
– Use NEMA-listed components and ensure grounding continuity.
European Union
– Must meet Low Voltage Directive (LVD) and EMC Directive.
– CE marking required; tested to EN 60309 (industrial) or EN 50075 (domestic).
Australia/New Zealand
– AS/NZS 3112 and AS/NZS 3123 govern plug and socket safety.
– RCM (Regulatory Compliance Mark) mandatory for electrical goods.
United Kingdom
– Post-Brexit, UKCA marking is required (though CE still accepted until 2025).
– Comply with BS 1363 and BS 546 as applicable.
Best Practices for Global Deployment
- Design for Flexibility: Offer modular power cords or field-replaceable plugs.
- Partner with Local Experts: Engage certified electricians or compliance consultants in target markets.
- Conduct On-Site Audits: Verify socket types and circuit availability before installation.
- Update Documentation: Maintain compliance records and update labels with regional requirements.
Conclusion
Successfully managing logistics and compliance for 240-volt plug types requires understanding regional electrical standards, planning for international compatibility, and adhering to local safety regulations. By selecting the correct plug types, ensuring proper documentation, and engaging with compliance experts, businesses can minimize risk, reduce downtime, and ensure safe, reliable operation across global markets.
Conclusion: Sourcing 240-Volt Plug Types
In conclusion, sourcing the correct 240-volt plug type requires careful consideration of regional standards, appliance requirements, and safety regulations. The most common plug types for 240-volt systems vary significantly by country—such as NEMA 6-15 or 6-20 in North America, Type G in the UK, Type F (Schuko) in many parts of Europe, and AS/NZS 3112 in Australia and New Zealand. Ensuring compatibility between the plug, socket, and electrical system is essential to guarantee safe and efficient operation.
When sourcing 240-volt plugs or adapters, it is critical to verify voltage and current ratings, grounding requirements, and certification standards (e.g., UL, CE, CSA, or SAA). Using inappropriate or unverified components can lead to equipment damage, fire hazards, or personal injury. For international applications, using locally certified power cords or hardwiring through a qualified electrician is often the safest and most compliant approach.
Ultimately, proper identification of the required plug type based on geographical location and equipment specifications, combined with adherence to local electrical codes, ensures reliable and safe use of 240-volt electrical systems.