The global transformer market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing electricity demand, grid modernization initiatives, and the integration of renewable energy sources. According to Grand View Research, the global power transformer market size was valued at USD 42.3 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1% from 2023 to 2030. Similarly, Mordor Intelligence projects a CAGR of over 6.8% during the forecast period of 2023–2028, with rising industrialization and investments in smart grid infrastructure acting as key growth catalysts. Within this expanding landscape, 240/208V transformers—commonly used in commercial and industrial applications for step-down voltage conversion—have become critical components in reliable power distribution systems. As demand for efficient, compact, and NEMA-compliant transformers grows, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in product innovation, energy efficiency, and global supply chain reach. The following list highlights the top seven manufacturers shaping the 240/208V transformer segment through technological advancement and proven market performance.
Top 7 240 208 Transformer Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 PowerVolt Group
Domain Est. 2020
Website: powervoltgroup.com
Key Highlights: PowerVolt Group is a leading U.S. manufacturer of industrial and commercial transformers and linear DC power supplies. Over 5000 standard and custom ……
#2 3
Domain Est. 1997
#3 Transformer (208/240
Domain Est. 1998
Website: supplyhouse.com
Key Highlights: Free delivery over $99 90-day returnsS8407-034 is is an official OEM Transformer (208/240-24V, 40VA) for Bard HVAC equipment. Specs. –. VA Rating: 40….
#4 Transformers
Domain Est. 1990
Website: electrification.us.abb.com
Key Highlights: ABB’s type QL K-Factor transformers are designed to withstand the additional heating that accompanies the presence of harmonics in electrical systems….
#5 Low Voltage Distribution Transformer
Domain Est. 1995
Website: store.hubbell.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsLow Voltage Distribution Transformer – Single Phase, 240X480 – 120/240V, 15kVA · $1,992.16 ; Low Voltage Distribution Transformer – Single Phase, 240X480 – 120/ ……
#6 Armstrong Air 13H2801 208
Domain Est. 2001
Website: afsupply.com
Key Highlights: In stock Rating 5.0 1 Armstrong Air 13H2801 208 – 240 Voltage Transformer · Afue: Footed. Voltage: 240 Voltage. Width Inches: 3.16″. Height Inches: 3″. : 95% · Voltage: 120 Volta…
#7 30 kVA 240 Volt to 208 Volt Three phase Autotransformer RC30C
Domain Est. 2008
Website: canadatransformers.com
Key Highlights: Three phase Autotransformer RC30C-B has common primary-secondary windings which are not insulated from each other, offers no interference or disturbance ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 240 208 Transformer

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 240V 208V Transformers
As the global energy landscape evolves toward greater efficiency, digitalization, and sustainability, the market for electrical distribution equipment—including 240V to 208V step-down transformers—is expected to experience notable shifts by 2026. These transformers are commonly used in commercial, industrial, and institutional applications to adapt higher voltage supplies (240V) to standard 208V three-phase systems that power HVAC units, servers, lighting, and other critical equipment. Below is an analysis of key market trends shaping the demand and development of 240V 208V transformers in 2026.
1. Rising Demand from Data Centers and Edge Computing
The explosive growth of artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and edge data centers is driving increased need for reliable and efficient power distribution. Many of these facilities operate on 208V systems due to compatibility with IT equipment and energy efficiency. As new data centers are built and existing ones upgraded in 2026, demand for compact, high-efficiency 240V/208V transformers—especially low-profile and modular designs—is expected to rise significantly.
2. Emphasis on Energy Efficiency and Regulatory Compliance
Energy efficiency regulations—including updated DOE (U.S. Department of Energy) standards and international equivalents like the EU’s Ecodesign Directive—are pushing manufacturers to produce transformers with lower no-load and load losses. By 2026, the market will favor high-efficiency (e.g., DOE 2016-compliant or NEMA Premium) 240V 208V transformers, particularly in commercial buildings and industrial facilities aiming to meet sustainability goals and reduce operational costs.
3. Growth in Smart Grid and Building Automation Integration
The integration of smart building systems and IoT-enabled power management is influencing transformer design. In 2026, expect increased demand for 240V/208V transformers equipped with monitoring capabilities (e.g., temperature sensors, current meters, and communication interfaces). These “smart transformers” allow for predictive maintenance, load balancing, and remote diagnostics, improving system reliability and energy management.
4. Expansion of Renewable Energy and Microgrids
As businesses and municipalities adopt solar, wind, and energy storage systems, microgrid deployments are growing. These systems often require voltage transformation between different distribution levels. 240V/208V transformers play a key role in connecting renewable sources to local 208V loads. The 2026 market will see increased use of these transformers in hybrid power systems, especially in industrial parks and campus environments.
5. Supply Chain Localization and Reshoring
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions have prompted a shift toward regional manufacturing. In North America and Europe, there is growing preference for domestically produced transformers to ensure reliability and reduce lead times. By 2026, manufacturers of 240V 208V transformers are expected to expand local production capacity, supporting faster delivery and customization.
6. Advancements in Materials and Design
Transformer manufacturers are investing in amorphous metal cores, improved insulation materials, and compact designs to reduce size, weight, and losses. In 2026, these innovations will be particularly valuable in retrofit projects and urban installations where space and efficiency are critical.
7. Increased Demand in Retrofit and Modernization Projects
Much of the existing commercial and industrial infrastructure in North America was built with older electrical systems. As facilities upgrade to modern HVAC, lighting, and IT systems—often requiring 208V power—there is a growing need for 240V/208V step-down transformers. The 2026 market will benefit from this ongoing modernization cycle, especially in healthcare, education, and government sectors.
Conclusion
By 2026, the market for 240V 208V transformers will be shaped by technological innovation, regulatory pressures, and evolving energy needs. Growth will be strongest in data centers, smart buildings, and renewable energy applications. Manufacturers that focus on efficiency, digital integration, and supply chain resilience will be best positioned to capture market share. As electrification and decarbonization accelerate, these transformers will remain a critical component in the modern electrical ecosystem.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 240V to 208V Transformer (Quality and IP)
Sourcing a 240V to 208V transformer may seem straightforward, but overlooking critical quality and Ingress Protection (IP) factors can lead to performance issues, safety hazards, or premature failure. Below are key pitfalls to avoid:
1. Ignoring Transformer Efficiency and Core Quality
One of the most common quality pitfalls is selecting a transformer based solely on price without evaluating core construction and efficiency. Low-cost units often use inferior-grade silicon steel or even recycled magnetic materials, leading to:
- Higher no-load and load losses
- Excessive heat generation
- Reduced lifespan and reliability
- Increased energy costs over time
Always verify efficiency ratings (e.g., DOE 2016 compliance in the U.S.) and request core material specifications from the supplier.
2. Overlooking Insulation Class and Thermal Rating
Transformers must operate reliably under load without overheating. A frequent oversight is neglecting the insulation class (e.g., 130°C, 150°C, 180°C). Using a transformer with inadequate thermal rating in a high-ambient environment can result in:
- Insulation breakdown
- Shortened service life
- Fire risk in extreme cases
Ensure the transformer’s insulation class matches the expected operating temperature and duty cycle.
3. Assuming All Transformers Are Suitable for Indoor/Outdoor Use
The Ingress Protection (IP) rating is critical for environmental compatibility. A common mistake is using an indoor-rated transformer (e.g., IP20) in outdoor or damp locations, leading to:
- Moisture ingress causing corrosion or short circuits
- Dust accumulation affecting cooling and electrical safety
- Premature failure due to environmental exposure
Always match the IP rating to the installation environment:
– IP20: Indoor, dry, clean environments
– IP54 or higher: Outdoor, dusty, or washdown areas
– IP65/IP66: Harsh industrial or wet locations
4. Failing to Verify Safety Certifications and Standards
Procuring uncertified or non-compliant transformers poses significant safety and legal risks. Avoid units lacking recognized certifications such as:
- UL/cUL (North America)
- CE (Europe)
- CSA (Canada)
- IEC standards (international)
Uncertified transformers may not meet dielectric strength, temperature rise, or construction requirements, increasing the risk of electrical hazards.
5. Underestimating Mechanical Build and Enclosure Quality
The physical construction impacts longevity and safety. Poor-quality enclosures may exhibit:
- Thin gauge steel prone to denting and corrosion
- Inadequate grounding points
- Poorly sealed knockouts or conduit entries
For outdoor or industrial applications, ensure the enclosure is robust, corrosion-resistant (e.g., powder-coated or stainless steel), and properly rated for the environment.
6. Neglecting Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) and Noise
Some low-quality transformers emit high electromagnetic interference (EMI) or audible hum due to loose windings or poor core lamination. This can disrupt sensitive equipment and violate EMC regulations in industrial or commercial settings. Verify low-noise design and shielding if used near control systems or offices.
7. Skipping Site-Specific Environmental Considerations
Even with the correct IP rating, other environmental factors are often ignored:
– Altitude (affects cooling and dielectric strength)
– Ambient temperature extremes
– Vibration or seismic requirements
Specify transformers rated for the actual installation conditions to ensure reliable operation.
Conclusion
Avoiding these pitfalls requires due diligence in evaluating both electrical quality and environmental protection (IP). Always source from reputable manufacturers, verify certifications, and match technical specifications precisely to the application. Investing in a high-quality, correctly rated transformer prevents costly downtime, safety incidents, and compliance issues.
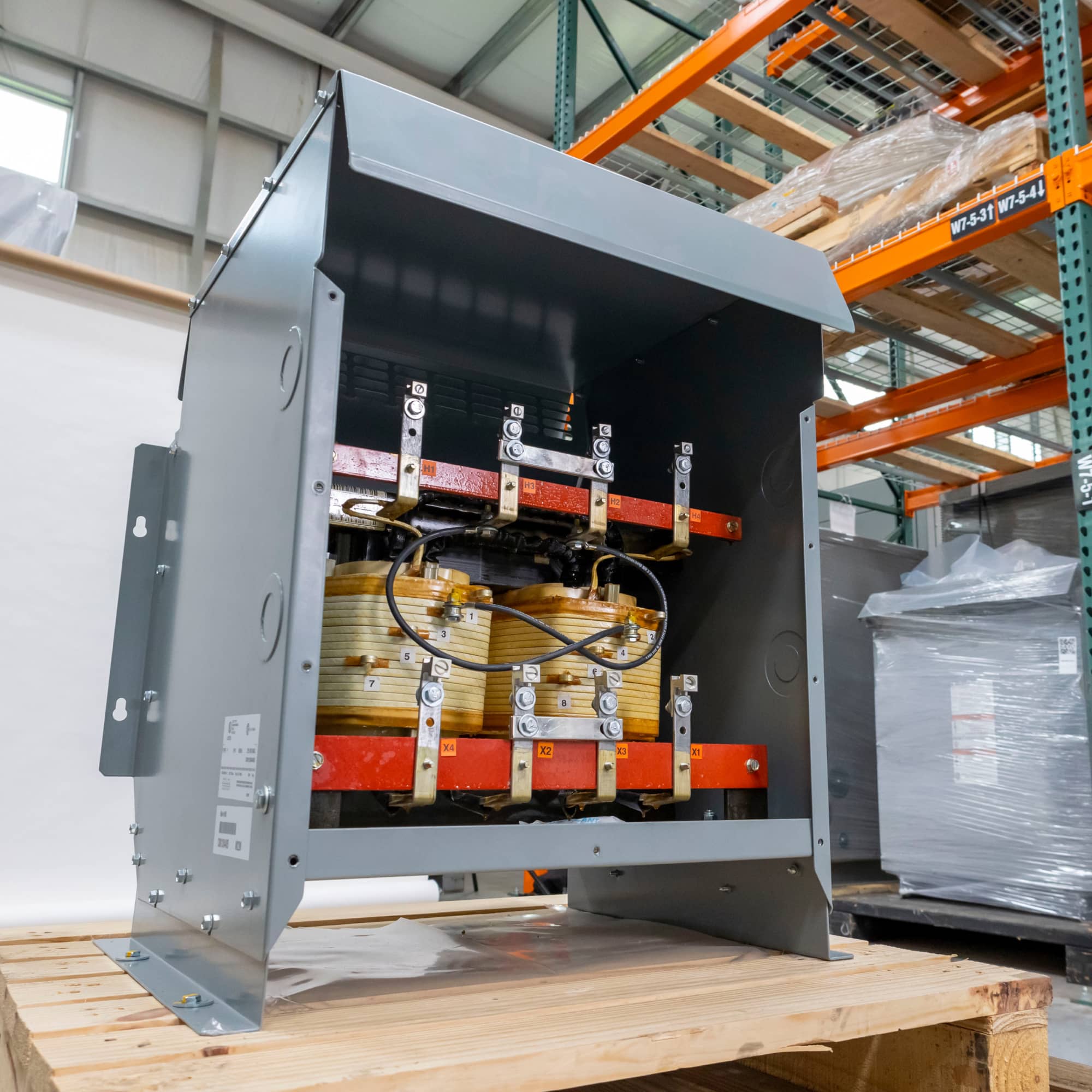

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 240V to 208V Transformer
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for transporting, installing, and operating a 240V to 208V step-down transformer. Adherence to these guidelines ensures safety, regulatory compliance, and optimal performance.
Shipping and Handling
- Packaging: Ensure the transformer is shipped in manufacturer-approved packaging with adequate cushioning to prevent damage during transit. Use skids or pallets for secure handling.
- Weight and Dimensions: Verify the unit’s weight and dimensions prior to shipment to select appropriate lifting equipment (e.g., forklifts, cranes) and ensure access through doorways and pathways.
- Lifting Points: Only use designated lifting lugs or hardware. Never lift by terminals, bushings, or enclosure.
- Orientation: Maintain upright orientation during transport. Tipping or laying the unit on its side may damage internal components or cause oil leakage in oil-filled models.
- Environmental Protection: Protect the unit from moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures during storage and transit. Avoid prolonged outdoor exposure.
Storage Requirements
- Indoor Storage: Store in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated indoor area when possible.
- Temperature Range: Maintain storage temperatures between -20°C and +40°C unless otherwise specified by the manufacturer.
- Elevation: Place on a level, stable surface. Use wooden blocks if stored directly on concrete to prevent moisture absorption.
- Duration: Limit long-term storage (over 6 months) without inspection. Check seals, insulation resistance, and desiccant (if applicable) before installation.
Installation Compliance
- Electrical Codes: Installation must comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 450 (Transformers and Transformer Vaults), local building codes, and utility requirements.
- Clearances: Maintain required clearances for ventilation and servicing as specified by NEC and manufacturer (e.g., 3 ft front, 1 ft sides, 12 in above).
- Grounding: Bond the transformer enclosure and neutral point (if applicable) to the facility grounding electrode system per NEC Article 250.
- Overcurrent Protection: Install primary and secondary overcurrent protection devices sized per NEC Table 450.3(B), considering transformer full-load current and inrush characteristics.
- Ventilation: Provide adequate airflow for cooling, especially for ventilated dry-type units. Avoid confined or enclosed spaces without forced ventilation.
Safety and Environmental Compliance
- NFPA 70E: Follow arc flash and electrical safety standards during installation and maintenance. Use appropriate PPE when working near energized components.
- UL/cUL Certification: Verify the transformer is certified to UL 506 (Standard for Safety of Specialty Transformers) or equivalent for use in North America.
- RoHS/REACH Compliance: Confirm the unit complies with environmental directives restricting hazardous substances (if applicable, especially for international shipments).
- Oil Containment (if oil-filled): For oil-immersed units, ensure secondary containment (e.g., spill pallet) is provided and meets EPA Spill Prevention, Control, and Countermeasure (SPCC) requirements.
Documentation and Labeling
- Nameplate Data: Ensure the unit’s nameplate is legible and includes key information: kVA rating, input/output voltages (240V primary / 208V secondary), frequency (60 Hz), impedance, serial number, and manufacturer.
- Compliance Labels: Verify presence of certification marks (e.g., UL, CSA, ETL) and proper NEMA enclosure rating (e.g., NEMA 1 for indoor, NEMA 3R for outdoor).
- Installation Manual: Retain and follow the manufacturer’s installation, operation, and maintenance (IOM) manual.
- Permits and Inspections: Obtain required electrical permits and schedule inspections by the Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ).
Operational and Maintenance Compliance
- Load Management: Operate within the rated kVA and temperature rise limits. Avoid sustained overloading.
- Routine Inspections: Conduct periodic visual and thermal inspections for signs of overheating, corrosion, or damage.
- Preventive Maintenance: Follow manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules, including insulation resistance testing (megger testing) and terminal torque checks.
- Record Keeping: Maintain logs of inspections, maintenance, and repairs for compliance audits and warranty tracking.
Adherence to this guide ensures safe, reliable, and code-compliant operation of the 240V to 208V transformer throughout its service life. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and local regulations for project-specific requirements.
Conclusion for Sourcing a 240V to 208V Transformer:
After evaluating the technical requirements, availability, and cost factors, sourcing a transformer to step down 240V to 208V is both feasible and practical for applications requiring compatibility with 208V equipment. Suitable single-phase or three-phase transformers are readily available from reputable electrical suppliers and manufacturers, with options that meet efficiency, safety, and regulatory standards such as UL, CSA, and DOE compliance.
Key considerations in the sourcing process include load requirements (kVA rating), efficiency, physical footprint, mounting type (encapsulated, dry-type, or pad-mounted), and environmental conditions. Additionally, lead times, warranty, and technical support should be factored into the final decision.
Procuring a properly sized and certified 240V to 208V transformer ensures stable voltage conversion, protects sensitive equipment, and enhances system reliability. With multiple suppliers offering competitive pricing and reliable delivery, the project can proceed confidently, knowing that the correct transformer solution is both accessible and cost-effective.