The global sheet metal fabrication market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by rising demand across industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global sheet metal fabrication market was valued at approximately USD 431.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 5.8% from 2024 to 2029. With increased industrialization and advancements in manufacturing technologies, gauge-specific products like 20 gauge sheet metal—known for its optimal balance of strength and formability—have become critical components in both heavy and light industrial applications. As demand rises, manufacturers specializing in precision sheet metal thicknesses are scaling capacity, enhancing material quality, and investing in sustainable production methods to meet evolving industry standards. This growing market landscape sets the stage for the emergence of key players leading innovation and reliability in 20 gauge sheet metal production.
Top 9 20 Gauge Sheet Metal Thickness Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
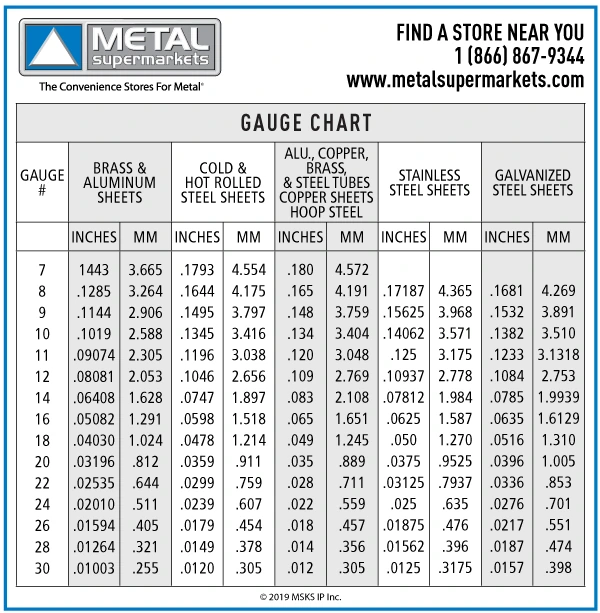
#1 Sheet Metal Gauge Chart
Domain Est. 1996
Website: metalsupermarkets.com
Key Highlights: A gauge conversion chart can be used to determine the actual thickness of sheet metal in inches or millimeters….
#2 Quality Cold Rolled Sheets
Domain Est. 1996
Website: bobcometal.com
Key Highlights: $450 delivery 17-day returnsBobco Metals provides businesses and home users with fast, easy and quality Cold Rolled Sheets – 20 Gauge supplies in Los Angeles, CA, USA….
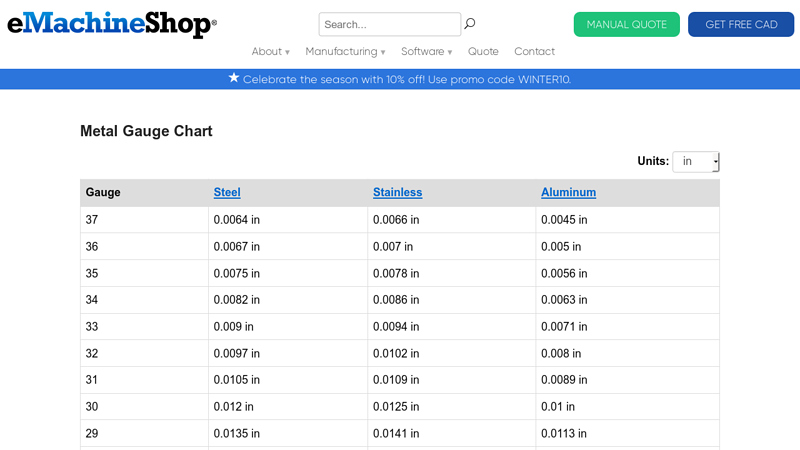
#3 Metal Gauge Chart
Domain Est. 1999
Website: emachineshop.com
Key Highlights: Metal Gauge Chart – Get engineering information at our online machineshop….
#4 20 ga 60″ x 120″ Galvanized Steel Sheets ASTM
Domain Est. 1999
Website: industrialmetalsupply.com
Key Highlights: Rating 4.5 (96) · 30-day returnsGalvanized steel sheets are available in several sizes and styles, offering enhanced strength and corrosion resistance to meet your application …
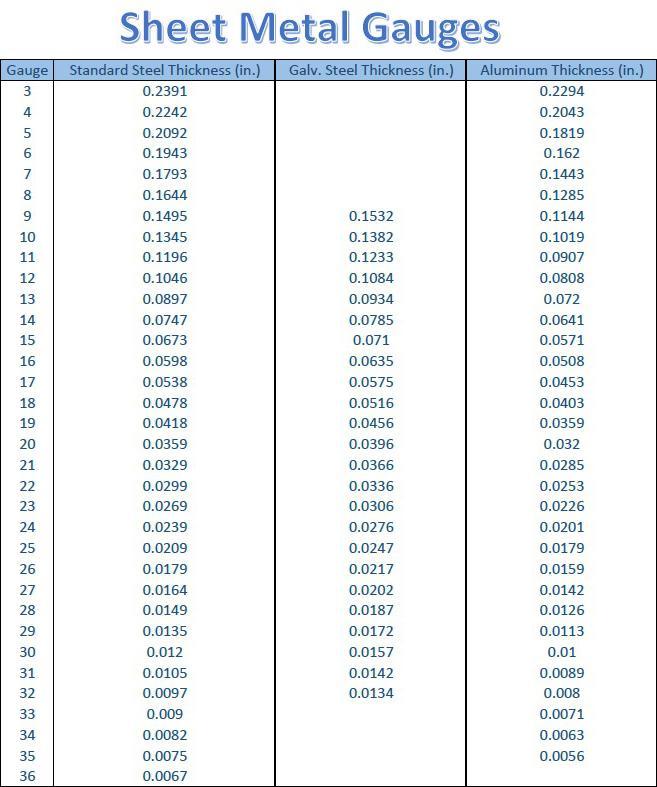
#5 Sheet Metal & Wire Gauge Sizes Table Chart
Domain Est. 2000
Website: engineersedge.com
Key Highlights: The following sheet metal gauge size reference chart gives the weight and thickness of sheet metal given as a gauge (sometimes spelled gage)…
#6 Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet (GI)
Domain Est. 2001
Website: madar.com
Key Highlights: High-quality hot-dip galvanized steel sheets (GI) conforming to ASTM A653 standards. Available in various sizes, thicknesses, and G90, G60, G20 ……
#7 Cold Rolled Steel
Domain Est. 2001
Website: protocase.com
Key Highlights: Stocked Gauges ; 14 gauge, 48″ x 96″ x 0.075″, 0.075″ ; 16 gauge, 48″ x 96″ x 0.060″, 0.06″ ; 18 gauge, 48″ x 96″ x 0.048″, 0.048″ ; 20 gauge, 48″ x 96″ x 0.036″ ……
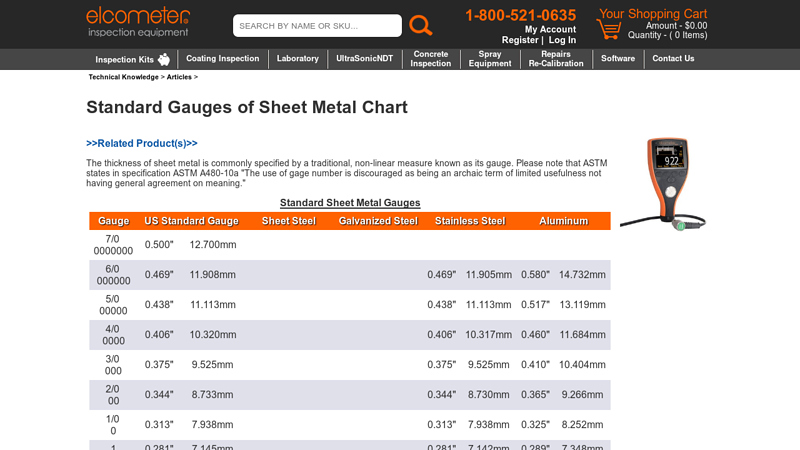
#8 Standard Gauges of Sheet Metal Chart
Domain Est. 2005
Website: elcometerusa.com
Key Highlights: Find the proper measurement for your gauge size. This chart compares gage numbers to their steel and aluminum sizing standards….
#9 Sheet Metal Gauge Size Chart
Domain Est. 2006
Website: custompartnet.com
Key Highlights: Comprehensive sheet metal gauge size chart for manufacturing and fabrication. Includes thickness and weight conversions for standard steel, galvanized steel ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 20 Gauge Sheet Metal Thickness
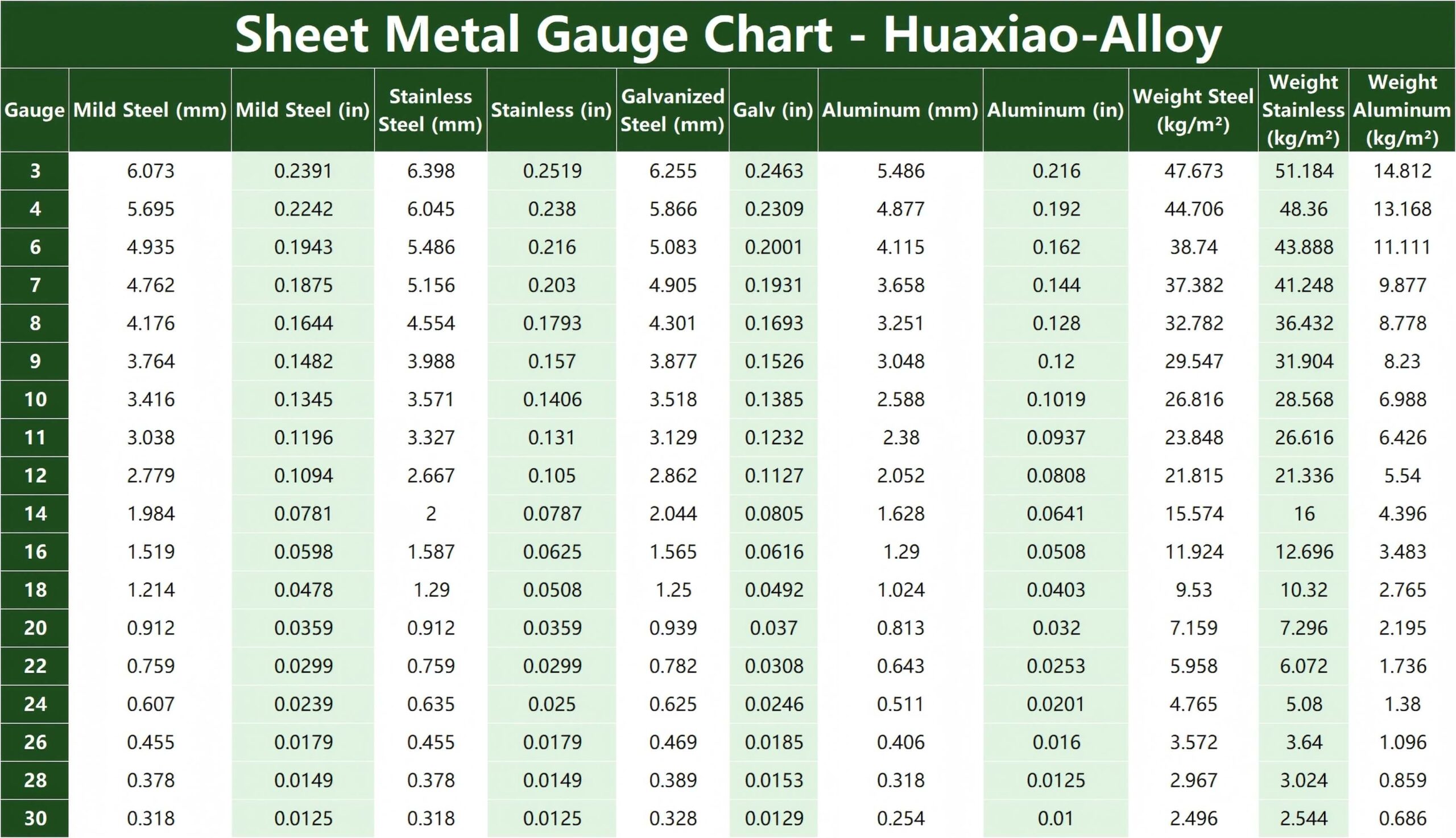
2026 Market Trends for 20 Gauge Sheet Metal Thickness
The 20 gauge (approximately 0.0359 inches or 0.91 mm thick) sheet metal segment is a vital component across numerous industries due to its optimal balance of strength, formability, and weight. As we approach 2026, several key trends are shaping the demand, production, and application of this specific thickness.
Rising Demand in Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Construction
The construction sector continues to be a major consumer of 20 gauge sheet metal, particularly in roofing, siding, HVAC ductwork, and structural supports. With global emphasis on green building standards—such as LEED and BREEAM—there is increasing demand for durable, recyclable materials. 20 gauge steel and aluminum, often coated with reflective or corrosion-resistant finishes, are favored for energy-efficient commercial and residential buildings. Advancements in coating technologies are extending the lifespan of 20 gauge panels, reducing lifecycle costs and supporting sustainability goals.
Growth in Electric Vehicles and Lightweighting in Automotive
Although traditionally used in heavier automotive components, 20 gauge sheet metal is finding renewed relevance in electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing. As automakers seek cost-effective, moderately strong materials for non-structural enclosures, battery housings, and underbody shielding, 20 gauge steel and aluminum offer a favorable strength-to-cost ratio. Coupled with lightweighting initiatives, manufacturers are optimizing designs using high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels in 20 gauge form to reduce vehicle weight without sacrificing safety.
Expansion in Industrial and Commercial Equipment Manufacturing
The industrial equipment sector—including material handling systems, enclosures, shelving, and control panels—relies heavily on 20 gauge metal for its rigidity and ease of fabrication. With Industry 4.0 driving automation and smart manufacturing, demand for standardized, durable enclosures is rising. 20 gauge sheet metal is ideal for laser cutting, CNC bending, and welding processes, enabling rapid prototyping and scalable production. Increased investment in automation infrastructure globally is expected to bolster demand through 2026.
Shift Toward Advanced Coatings and Corrosion Resistance
End-users across sectors are demanding longer-lasting materials, especially in harsh environments. This has led to a surge in the use of advanced coatings—such as Galvalume, zinc-aluminum alloys, and polymer-based finishes—applied to 20 gauge substrates. These coatings enhance corrosion resistance, reduce maintenance, and are particularly beneficial in coastal, agricultural, and industrial settings. Suppliers are investing in continuous coating lines to meet these performance requirements efficiently.
Supply Chain Localization and Resilience
Ongoing geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions are prompting manufacturers to localize sourcing of raw materials. In North America and Europe, there is a push to source 20 gauge sheet metal from domestic or nearshore producers, reducing dependency on volatile international markets. This trend supports regional steel mini-mills and service centers, which offer just-in-time delivery and custom slitting of 20 gauge coils, improving supply chain responsiveness.
Technological Integration in Fabrication
Advancements in digital manufacturing—including AI-driven nesting software, robotic bending, and automated welding—are increasing the precision and efficiency of working with 20 gauge sheet metal. These technologies minimize material waste and labor costs, making 20 gauge an even more cost-effective choice for complex fabrications. As more job shops adopt Industry 4.0 tools, the barrier to high-mix, low-volume production decreases, broadening the application scope.
Conclusion
By 2026, the market for 20 gauge sheet metal is poised for steady growth, driven by sustainability mandates, technological innovation, and evolving manufacturing needs. Its versatility ensures continued relevance across construction, transportation, and industrial sectors. Producers and fabricators who invest in advanced materials, localized supply chains, and smart manufacturing technologies will be best positioned to capitalize on these trends.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 20 Gauge Sheet Metal (Quality and IP)
Sourcing 20 gauge sheet metal seems straightforward, but overlooking key quality and intellectual property (IP) considerations can lead to costly delays, performance issues, or legal exposure. Here are critical pitfalls to avoid:
Inadequate Material Specification and Certification
Failing to clearly define and verify material properties is a leading cause of quality failures. 20 gauge refers only to thickness (approximately 0.0359 inches or 0.912 mm), not composition or performance. Without proper specifications, you risk receiving substandard material. Always require mill test reports (MTRs) or certificates of conformance (CoC) that validate chemical composition, mechanical properties (like tensile strength and yield strength), and compliance with relevant standards (e.g., ASTM A1008 for cold-rolled steel). Assuming all 20 gauge steel is equivalent—regardless of grade (e.g., CQ, HSLA) or finish—can result in parts that fail under stress or corrode prematurely.
Overlooking Surface Finish and Tolerances
The surface condition and dimensional accuracy of 20 gauge sheet metal significantly impact manufacturability and final product quality. Common issues include inconsistent surface finishes (e.g., mill scale, oil residue, or uneven galvanization), which can interfere with welding, painting, or coating adhesion. Additionally, failing to specify tight thickness tolerances or flatness requirements may lead to fit-up problems during fabrication. Always define acceptable surface treatments (e.g., galvanized, pre-painted, bare) and enforce tolerance standards per ASTM or ISO to ensure consistency across batches.
Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability Gaps
Lack of visibility into the metal’s origin and processing history increases the risk of counterfeit or non-compliant materials entering your supply chain. Unreliable suppliers may source from unknown mills or fail to maintain proper documentation. This opacity also complicates compliance with environmental, safety, or industry-specific regulations (e.g., RoHS, REACH). Insist on full traceability—from raw material to finished sheet—and audit suppliers regularly to verify ethical sourcing and manufacturing practices.
Intellectual Property and Design Infringement Risks
When sourcing custom-fabricated components from 20 gauge sheet metal, IP risks emerge if design files or tooling are shared without safeguards. Suppliers may replicate your designs for competitors or claim ownership of tooling developed during production. Always use robust non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) and clearly define IP ownership in contracts. Avoid sharing full design files when partial data suffices, and consider watermarking or encrypting sensitive CAD models to prevent unauthorized use.
Failure to Validate Supplier Qualifications
Choosing a supplier based solely on price or lead time often sacrifices quality and reliability. Unqualified vendors may lack proper quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001 certification), in-house testing capabilities, or experience with your required fabrication processes (e.g., laser cutting, bending). Conduct thorough supplier audits, request samples for testing, and evaluate their process controls before committing to large orders. A low-cost supplier may end up costing more due to rework, delays, or field failures.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 20 Gauge Sheet Metal Thickness
Overview of 20 Gauge Sheet Metal
20 gauge sheet metal is a commonly used thickness in manufacturing, construction, and industrial applications. The actual thickness varies slightly depending on the material (e.g., steel, aluminum, stainless steel) due to differences in the gauge standard. For reference:
– Mild Steel: Approximately 0.0359 inches (0.912 mm)
– Stainless Steel: Approximately 0.0375 inches (0.953 mm)
– Aluminum: Approximately 0.0320 inches (0.813 mm)
Understanding these small variations is critical for design, fabrication, and compliance with industry standards.
Material Specifications and Standards
Ensure all 20 gauge sheet metal meets recognized industry standards to maintain quality and compliance:
– ASTM A1008/A1008M: Standard specification for cold-rolled steel sheet in coils and cut lengths.
– ASTM A240/A240M: For stainless steel sheet, including 20 gauge thickness.
– ASTM B209: Standard for aluminum and aluminum-alloy sheet and plate products.
– ISO 16610: Geometric product specifications related to surface texture, relevant for finished parts.
Material certifications (e.g., mill test reports) should accompany shipments for traceability and regulatory compliance.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging prevents damage during storage and transit:
– Stacking: Use edge protectors and interlayer paper or plastic to prevent scratching. Max stack height should not exceed 48 inches unless palletized securely.
– Palletization: Secure sheets on wooden or recyclable composite pallets with stretch wrap or strapping. Label each pallet with material type, gauge, dimensions, and handling instructions.
– Protection: Use VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitor) paper for carbon steel to prevent rust during long-term storage or humid transport.
– Handling Equipment: Use vacuum lifters or magnetic cranes (for ferrous metals) to avoid surface deformation.
Transportation and Logistics
Efficient and safe transport is essential:
– Weight Considerations: 20 gauge steel sheet weighs approximately 1.08 lbs/ft² (5.27 kg/m²). Accurate weight calculation ensures compliance with vehicle load limits and freight classing.
– Freight Classification: Under the NMFTA (National Motor Freight Classification), sheet metal typically falls under Class 70–85, depending on density and packaging. Confirm with carrier for accurate pricing.
– Mode of Transport: Suitable for truck, rail, and sea freight. For international shipments, use ISPM 15-compliant wooden pallets.
– Documentation: Include packing lists, commercial invoices, and certificates of compliance. For cross-border shipments, ensure HS codes are accurate (e.g., 7210.70 for flat-rolled carbon steel).
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Adhere to regional and international regulations:
– REACH & RoHS (EU): Verify that coatings or treatments on metal sheets do not contain restricted substances.
– OSHA (USA): Comply with workplace safety standards for handling and storage to prevent injuries from sharp edges.
– EPA Regulations: Manage metal scrap and cutting fluids according to environmental guidelines.
– Customs Compliance: For imported/exported materials, ensure adherence to country-specific import duties and anti-dumping regulations (e.g., U.S. Section 232 tariffs on steel).
Quality Control and Inspection
Implement checks at all stages:
– Incoming Inspection: Verify thickness using micrometers or ultrasonic gauges. Tolerance for 20 gauge steel is typically ±0.003 inches.
– Surface Quality: Check for scratches, dents, oil residue, or oxidation.
– Dimensional Accuracy: Confirm sheet dimensions (length, width) match purchase order specifications.
– Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): For critical applications, consider eddy current testing for cracks or inconsistencies.
Storage Guidelines
Proper storage prevents degradation:
– Environment: Store indoors in a dry, climate-controlled area. Relative humidity should be below 60% to prevent corrosion.
– Racking: Use horizontal racks with adequate support to prevent warping. Do not lean sheets vertically without proper backing.
– Separation: Isolate different metals (e.g., aluminum and steel) to avoid galvanic corrosion.
– Inventory Rotation: Follow FIFO (First In, First Out) to reduce risk of long-term storage issues.
Sustainability and Recycling
Promote environmentally responsible practices:
– Recyclability: 20 gauge sheet metal is 100% recyclable. Coordinate with certified recycling vendors.
– Waste Minimization: Optimize nesting in cutting processes to reduce scrap.
– Carbon Footprint: Choose suppliers with ISO 14001 certification and low-emission production methods.
Conclusion
Managing the logistics and compliance of 20 gauge sheet metal requires attention to material standards, safe handling, regulatory requirements, and environmental responsibility. By following this guide, businesses can ensure product integrity, reduce risks, and maintain efficient supply chain operations.
Conclusion for Sourcing 20 Gauge Sheet Metal Thickness:
After evaluating material specifications, availability, and supplier performance, sourcing 20-gauge sheet metal (approximately 0.0359 inches or 0.91 mm thick) proves to be a practical and widely accessible solution for applications requiring a balance of strength, formability, and weight efficiency. This thickness is commonly stocked by metal suppliers in various materials such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and galvanized options, making it versatile for industries including HVAC, automotive, electronics enclosures, and light manufacturing.
Sourcing 20-gauge sheet metal is cost-effective due to its standardization and compatibility with common fabrication processes like cutting, bending, and welding. However, it is essential to confirm precise thickness tolerances and material grade with suppliers to ensure consistency and meet project specifications. Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers who provide certification and consistent quality will enhance reliability in production and reduce material waste.
In summary, 20-gauge sheet metal is a well-supported, economical, and suitable choice for a broad range of applications, and its sourcing can be optimized through supplier vetting, volume negotiation, and attention to material standards.