The global hydraulic equipment market is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand across construction, agriculture, and industrial manufacturing sectors. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the hydraulic equipment market was valued at USD 33.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 4.5% from 2024 to 2029. A critical component within this ecosystem is the 2-way hydraulic valve, essential for controlling fluid flow and pressure in hydraulic systems. These valves are widely used in applications ranging from mobile machinery to factory automation, where reliability and precision are paramount. With increasing automation and infrastructure development worldwide, the demand for high-performance 2-way hydraulic valves is on the rise. This growth trajectory has spurred innovation and competition among manufacturers, leading to advancements in durability, energy efficiency, and integration with digital control systems. Based on market presence, product range, technological innovation, and global reach, the following eight companies have emerged as leading manufacturers of 2-way hydraulic valves.
Top 8 2 Way Hydraulic Valve Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 Hydraulic Cylinder Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1999
Website: cylval.com
Key Highlights: Cylinders & Valves, Inc. offers a wide variety of standard and custom hydraulic cylinders, pneumatic cylinders, replacement parts, and cylinder repair….
#2 VERSA – Valve Manufacturer
Domain Est. 1996
Website: versa-valves.com
Key Highlights: VERSA Products is a manufacturer of valves, controls and accessories engineered to outperform and outlast all others. Explore our flexible product lines….
#3 Atos Hydraulics EN
Domain Est. 1996
Website: atos.com
Key Highlights: We offer our customers a unique mix of electrohydraulic components for industrial, hazardous and corrosive environments….
#4 2
Domain Est. 2009
Website: winnerhydraulics.com
Key Highlights: Winner offers 2-way direct-acting control valves with various flow direction designs for controlling start, stop, and flow direction in industrial and ……
#5 Valve Manufacturer and Supplier
Domain Est. 2009
Website: valveman.com
Key Highlights: ValveMan delivers reliable valve solutions for every industry. Find top-quality ball valves, check valves, and more with fast shipping and expert support….
#6 Sun Hydraulics
Domain Est. 1994
Website: sunhydraulics.com
Key Highlights: QuickDesign streamlines your custom design process, delivering complete designs in as little as ten minutes….
#7 Valves
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ph.parker.com
Key Highlights: … 2) ZoomLock PUSH – Approved Refrigerants”,”document-type”:”Static File … Way & 3 Way Internal Pressures to 20,000 psi (1379 bar) Water Depth to ……
#8 Atlantic Fluid Tech
Domain Est. 2008 | Founded: 1979
Website: atlanticfluidtech.com
Key Highlights: Since 1979 Atlantic Fluid Tech has been designing and manufacturing in Italy hydraulic valves and integrated circuits….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 2 Way Hydraulic Valve

2026 Market Trends for 2-Way Hydraulic Valves
Market Overview and Growth Drivers
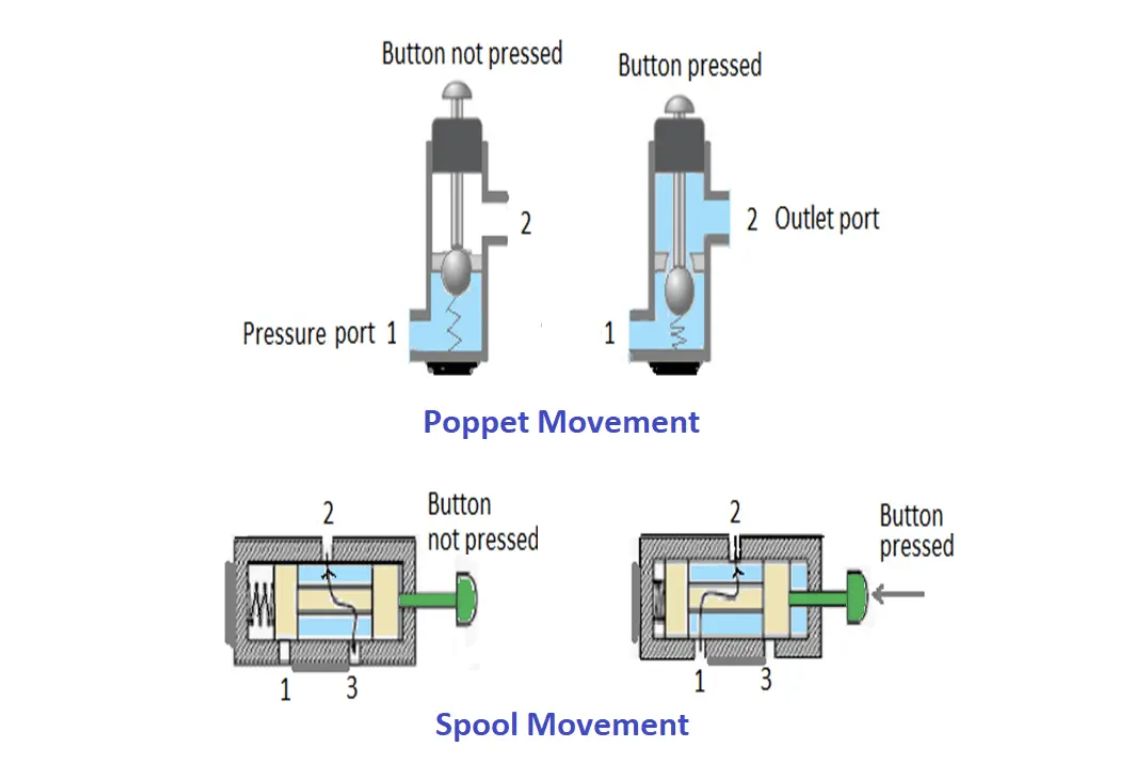
The global market for 2-way hydraulic valves is projected to experience steady growth by 2026, driven by increasing demand across industrial automation, construction, agriculture, and manufacturing sectors. As industries continue to emphasize efficiency, precision, and energy conservation, hydraulic systems—particularly those utilizing reliable and compact components like 2-way valves—are seeing renewed investment. The 2-way hydraulic valve, which controls fluid flow in a single path by opening or closing the circuit, remains a fundamental building block in hydraulic systems due to its simplicity, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Key drivers for market expansion include the global rise in infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies, and the ongoing modernization of industrial machinery. Additionally, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies is prompting upgrades in hydraulic control systems, where 2-way valves play a critical role in enabling responsive and automated operations.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
By 2026, technological innovation is expected to significantly influence the design and functionality of 2-way hydraulic valves. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on enhancing valve performance through materials science improvements, such as the use of corrosion-resistant alloys and advanced sealing technologies that extend operational life and reduce maintenance needs.
Moreover, smart hydraulic systems incorporating IoT-enabled sensors and digital monitoring are becoming more common. While traditionally simple, 2-way valves are now being designed with integrated electronics, allowing for remote operation, real-time diagnostics, and predictive maintenance. This shift supports broader trends toward smart factories and connected equipment, especially in sectors like automotive manufacturing and heavy machinery.
Miniaturization is another trend, with demand rising for compact, lightweight valves that maintain high flow efficiency. This is particularly relevant in mobile hydraulics, such as agricultural and construction vehicles, where space and weight constraints are critical.
Regional Market Dynamics
Geographically, the Asia-Pacific region is anticipated to lead the 2-way hydraulic valve market by 2026, fueled by rapid industrialization in countries like China, India, and Vietnam. Government investments in infrastructure and smart manufacturing initiatives are creating substantial demand for hydraulic components. Meanwhile, North America and Europe are focusing on sustainability and energy-efficient systems, driving the adoption of high-performance and low-leakage valves.
In Europe, regulatory frameworks such as the EU Ecodesign Directive are pushing manufacturers to develop hydraulic components that minimize energy loss and environmental impact. This regulatory environment is accelerating the shift toward efficient 2-way valve designs that reduce pressure drops and internal leakage.
Competitive Landscape and Key Players
The competitive landscape for 2-way hydraulic valves remains fragmented, with a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized regional manufacturers. Key players such as Bosch Rexroth, Parker Hannifin, Danfoss, and Eaton are investing heavily in R&D to differentiate their products through enhanced reliability, digital integration, and customizability.
By 2026, partnerships between hydraulic component suppliers and machine OEMs are expected to increase, enabling co-development of optimized hydraulic circuits. This collaborative approach supports faster innovation cycles and ensures compatibility with next-generation machinery platforms.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is emerging as a critical factor shaping the 2026 market. Hydraulic systems are under scrutiny for their energy consumption and potential for fluid leakage. In response, manufacturers of 2-way valves are prioritizing eco-design principles—reducing material use, improving recyclability, and enhancing sealing performance to prevent hydraulic fluid loss.
Biodegradable hydraulic fluids are gaining traction, and valve materials are being adapted to remain compatible with these environmentally friendly alternatives. This trend aligns with corporate sustainability goals and stricter environmental regulations, particularly in Europe and North America.
Conclusion
By 2026, the 2-way hydraulic valve market will be characterized by technological integration, regional growth imbalances, and a strong emphasis on efficiency and sustainability. While the fundamental role of the 2-way valve remains unchanged, its evolution into smarter, more efficient, and environmentally compatible components will ensure its continued relevance in modern hydraulic systems. Companies that invest in innovation, digital capabilities, and sustainable manufacturing practices are likely to gain a competitive advantage in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls Sourcing 2-Way Hydraulic Valves (Quality & IP Rating)
Sourcing 2-way hydraulic valves requires careful attention to avoid performance issues, safety hazards, and costly downtime. Here are the most common pitfalls related to quality and Ingress Protection (IP) rating:
Inadequate Quality Control and Material Selection
- Substandard Materials: Choosing valves made from inferior metals (e.g., low-grade steel, poor-quality brass) or seals (e.g., non-hydraulic-grade elastomers) leads to premature wear, corrosion, leaks, and failure under pressure or temperature extremes.
- Poor Manufacturing Tolerances: Inconsistent machining or assembly results in internal leakage (bypass), inconsistent actuation, reduced efficiency, and shortened lifespan. Precision-ground spools and bores are critical.
- Lack of Certification and Testing: Suppliers failing to provide proof of pressure testing, material certifications (e.g., RoHS, REACH), or compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO 4413, ISO 1179) increase the risk of receiving non-conforming products.
- Counterfeit or Grey Market Goods: Sourcing from unreliable channels risks receiving fake or refurbished valves misrepresented as new, lacking traceability and warranty support.
Misunderstanding or Mismatching IP (Ingress Protection) Rating
- Ignoring Environmental Needs: Selecting a valve with insufficient IP rating (e.g., IP65 instead of IP67/IP69K) for harsh environments (dust, moisture, washdowns, outdoor use) leads to internal contamination, corrosion, electrical failures (for solenoid valves), and premature failure.
- Over-Specifying IP Rating: Choosing an unnecessarily high IP rating (e.g., IP69K for a clean indoor environment) increases cost without adding value and may complicate maintenance or heat dissipation.
- Confusing IP Rating with Pressure Rating: Mistaking IP (protection against solids/liquids) for the valve’s pressure rating (maximum operating pressure) can lead to catastrophic failure if the valve is used beyond its pressure limits.
- Neglecting Installation and Maintenance Impact: Even a high IP-rated valve can be compromised by improper installation (damaged seals, incorrect conduit entry), damaged cables, or poor maintenance practices, negating the intended protection.
Overlooking Compatibility and Application Requirements
- Fluid Compatibility: Failing to verify seal and material compatibility with the specific hydraulic fluid (e.g., HFC, HFD, biodegradable oils) causes seal swelling, degradation, and leaks.
- Pressure and Flow Mismatch: Selecting a valve with inadequate pressure rating or flow capacity (Cv/Kv) results in poor system performance, cavitation, overheating, or valve damage.
- Voltage and Coil Compatibility: For solenoid valves, using the wrong voltage, coil type (AC/DC), or duty cycle leads to coil burnout, failure to actuate, or excessive heat generation.
Relying Solely on Price as the Decision Factor
- Prioritizing Low Cost Over Long-Term Value: The cheapest valve often has hidden costs due to frequent failures, downtime, maintenance, and potential system damage. Investing in quality upfront ensures reliability and lower total cost of ownership.
- Lack of Supplier Vetting: Choosing suppliers based only on price without evaluating their reputation, technical support, lead times, and warranty terms increases supply chain risk.
By understanding and proactively addressing these common pitfalls—especially concerning material quality, manufacturing standards, and the correct IP rating for the operating environment—buyers can ensure the reliable, safe, and efficient performance of their hydraulic systems.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 2-Way Hydraulic Valve
Overview
A 2-way hydraulic valve is a fundamental component in fluid power systems, used to control the flow of hydraulic fluid by opening, closing, or redirecting flow paths. Proper logistics and compliance management are essential to ensure safe transportation, regulatory adherence, and efficient integration into industrial applications.
Classification & HS Code
- Product Type: Hydraulic Control Valve (2-Way)
- HS Code (Harmonized System): 8481.80
- Note: This code generally applies to valves for pipes, boiler shells, tanks, or fluid tanks, including pressure-reducing valves and thermostatically controlled valves. Confirm with local customs authorities, as sub-classifications may vary by region (e.g., 8481.80.50 in the U.S. for industrial hydraulic valves).
Packaging & Handling Requirements
- Packaging:
- Use protective packaging (e.g., sealed plastic bags, foam inserts) to prevent contamination from dust, moisture, or debris.
- Secure valves in sturdy corrugated cardboard or wooden crates for bulk shipments.
- Mark packages with “Fragile,” “Do Not Stack,” and orientation arrows if applicable.
- Handling:
- Avoid dropping or impact to prevent internal damage to seals and spools.
- Store in a dry, temperature-controlled environment (typically 0°C to 40°C).
- Keep ports capped or sealed to prevent ingress of foreign particles.
Shipping & Transportation
- Modes of Transport: Suitable for air, sea, and ground freight.
- Documentation:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading (B/L) or Air Waybill (AWB)
- Certificate of Origin (if required for trade agreements)
- Special Considerations:
- Valves containing residual oil or hydraulic fluid may be subject to IATA/IMDG regulations if quantities exceed thresholds.
- Confirm with carriers whether valves are classified as hazardous due to lubricants or materials (e.g., brass containing lead).
Regulatory Compliance
- REACH (EU):
- Ensure compliance with Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals.
- Disclose Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) if present (e.g., lead in brass components).
- RoHS (EU):
- Comply with restrictions on hazardous substances (e.g., lead, cadmium) in electrical/electronic components if the valve includes solenoid actuation.
- TSCA (USA):
- Confirm compliance with the Toxic Substances Control Act, particularly for chemical content in materials.
- CE Marking (EU):
- Required if the valve is part of a machinery system covered under the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC).
- Pressure Equipment Directive (PED 2014/68/EU):
- May apply if the valve is used in pressurized systems above specified thresholds. Classify under Article 4 and determine conformity assessment procedure.
Import/Export Controls
- Export Regulations:
- Check EAR (Export Administration Regulations, USA) for potential dual-use concerns (unlikely for standard 2-way valves, but verify if designed for military or aerospace use).
- Import Requirements:
- Verify country-specific standards (e.g., GOST in Russia, CCC in China) if applicable.
- Some countries require testing/certification by local authorities (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil).
Environmental & Safety Considerations
- End-of-Life Disposal:
- Follow WEEE (EU) guidelines if the valve contains electronic components.
- Recycle metal components (steel, brass, aluminum) according to local waste regulations.
- Leakage Prevention:
- Ensure valves are depressurized and drained before shipment to avoid environmental hazards.
Documentation & Record Keeping
- Maintain records for:
- Material Declarations (REACH, RoHS)
- Conformity Assessments (CE, PED)
- Shipping manifests and customs filings (minimum 5 years, per international standards)
- Provide technical data sheets (TDS) and safety data sheets (SDS) if lubricants or coatings are present.
Best Practices
- Partner with freight forwarders experienced in industrial components.
- Label valves with part number, batch/lot code, and compliance marks.
- Conduct periodic audits of supply chain compliance, especially for evolving regulations.
By adhering to this guide, manufacturers, distributors, and importers can ensure smooth logistics operations and full compliance for 2-way hydraulic valves across global markets.
Conclusion for Sourcing a 2-Way Hydraulic Valve:
After a comprehensive evaluation of technical specifications, supplier reliability, cost, lead times, and product quality, sourcing a 2-way hydraulic valve requires a balanced approach that prioritizes performance, durability, and long-term operational efficiency. It is essential to select a valve that meets the required pressure ratings, flow capacity, and compatibility with the hydraulic system’s fluid and operating environment. Partnering with reputable manufacturers or suppliers who adhere to international standards (such as ISO certifications) ensures reliability and after-sales support.
Additionally, considering factors such as energy efficiency, ease of installation, and maintenance requirements will contribute to minimizing downtime and reducing total cost of ownership. Whether opting for a solenoid-operated, manually actuated, or pilot-operated valve, aligning the valve characteristics with the application’s demands is critical.
In conclusion, successful sourcing involves not only competitive pricing but also assurance of quality, technical support, and supply chain consistency. A well-informed decision will enhance system performance, safety, and longevity, making the 2-way hydraulic valve a reliable component within the broader hydraulic system.