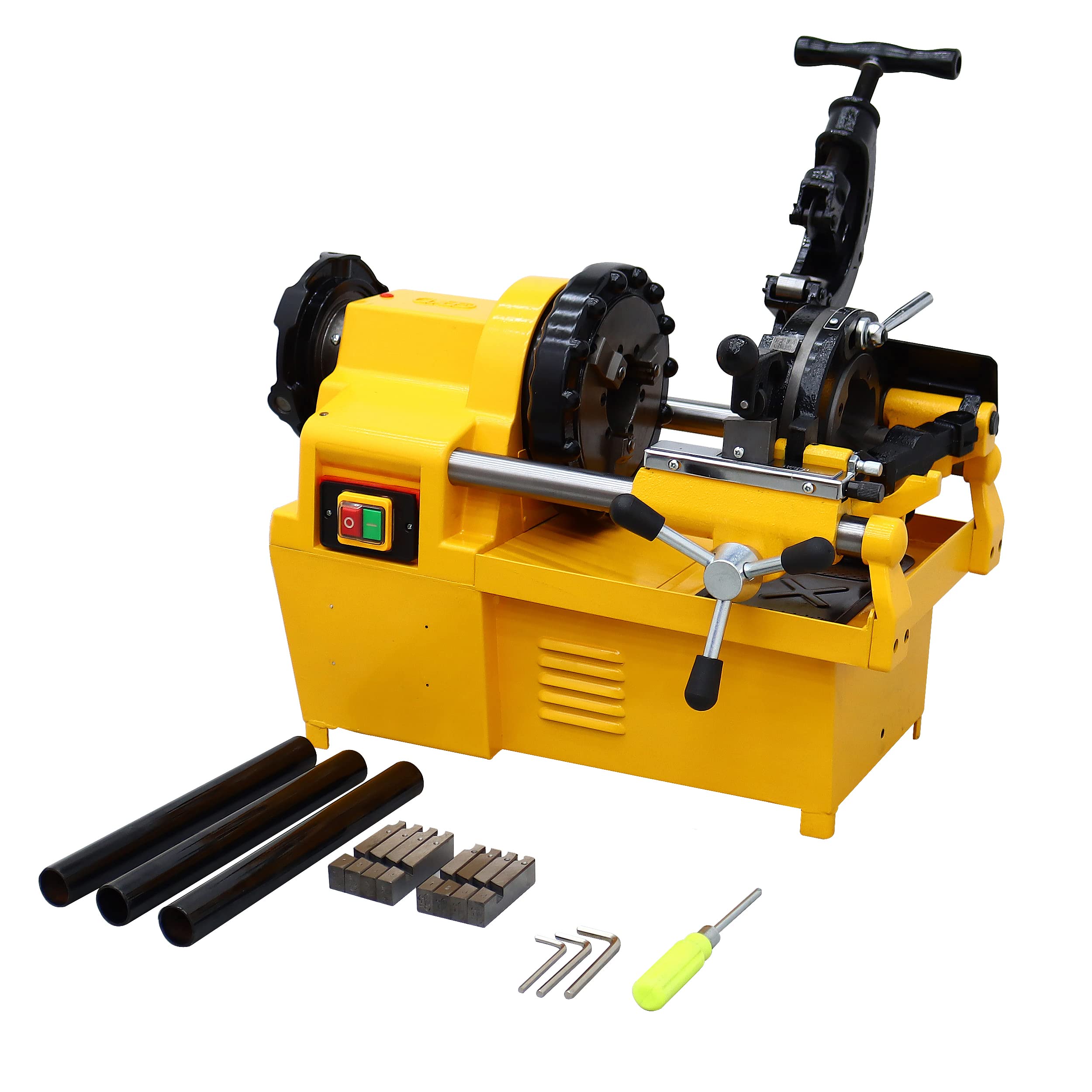
The global pipe threader market is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing demand across construction, oil & gas, plumbing, and industrial maintenance sectors. According to Grand View Research, the global pipe processing equipment market—which includes threaders, cutters, and benders—was valued at approximately USD 3.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. Factors such as rising infrastructure development, stringent pipeline safety regulations, and the need for efficient on-site plumbing solutions are fueling adoption of high-precision threaders. Mordor Intelligence further supports this trajectory, noting sustained growth in the North American and Asia-Pacific regions due to urbanization and industrial modernization efforts. As demand for reliable and efficient 2″ pipe threaders climbs, manufacturers are innovating with enhanced durability, portability, and motor efficiency. In this competitive landscape, seven key players have emerged as leaders, combining engineering excellence with global reach to meet the evolving needs of professional contractors and industrial users alike.
Top 7 2 Pipe Threader Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 OSG USA, INC.
Domain Est. 2000
Website: osgtool.com
Key Highlights: OSG is a leading manufacturer of taps, end mills, drills and thread-making tools. We offer an extensive line of high technology cutting tools featuring ……
#2 Pipe Threaders
Domain Est. 1995
Website: ridgid.com
Key Highlights: RIDGID pipe threaders bring confidence and precision when joining, forming or connecting pipe. Shop our line of manual and power threaders and accessories….
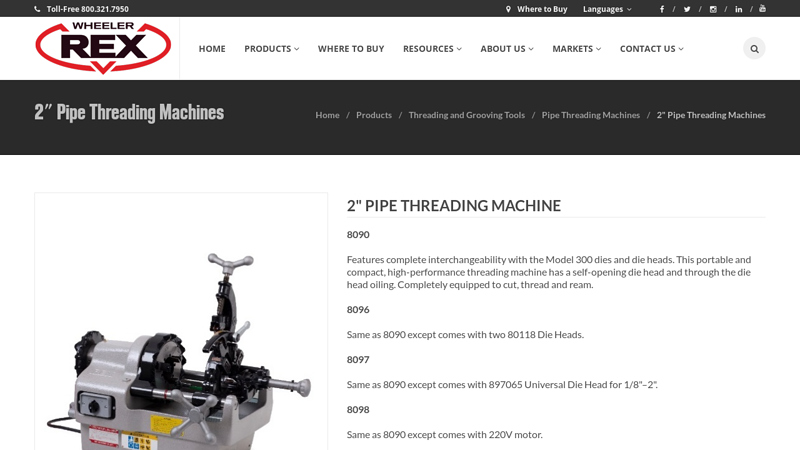
#3 The hardest working 2″ pipe threading machines
Domain Est. 1996
Website: wheelerrex.com
Key Highlights: This portable and compact, high-performance threading machine has a self-opening die head and through the die head oiling. Completely equipped to cut, thread ……
#4 Pipe Threaders & Pipe Threading Machines @ Ferguson.com
Domain Est. 1996
#5 Oster Manufacturing Company
Domain Est. 1999
Website: ostermfg.com
Key Highlights: Since 1893, the Oster Manufacturing Company has been producing the highest quality and longest-lasting pipe threading and bolt threading machines on the market….
#6 Advanced Pipe Threading & CNC Machine Tools for Global …
Domain Est. 2002
Website: pmc-colinet.com
Key Highlights: Our cutting-edge, customizable CNC threading and machine tools are designed to optimize performance and reduce downtime in your production line….
#7 Pipe Threading Machine
Domain Est. 2011
Expert Sourcing Insights for 2 Pipe Threader

H2: 2026 Market Trends for 2-Inch Pipe Threaders
The global market for 2-inch pipe threaders is expected to undergo significant transformation by 2026, driven by advancements in technology, evolving construction and infrastructure demands, and shifting industrial priorities. As a critical tool in plumbing, HVAC, oil and gas, and industrial maintenance sectors, 2-inch pipe threaders are seeing increased demand due to their role in large-diameter pipe installations. Below are the key market trends shaping the industry:
-
Rise in Infrastructure Development
Governments worldwide are investing heavily in water supply systems, wastewater management, and urban development projects. These initiatives are creating sustained demand for large-diameter pipe installation tools, including 2-inch pipe threaders. Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are particularly active, fueling market growth. -
Adoption of Cordless and Battery-Powered Models
By 2026, the shift toward cordless, battery-operated pipe threaders is accelerating. Technological improvements in lithium-ion batteries have enhanced portability, runtime, and power efficiency. Contractors increasingly prefer cordless models for their flexibility in remote or confined job sites, reducing reliance on generators and extension cords. -
Integration of Smart Technology and IoT
Leading manufacturers are incorporating smart features such as torque monitoring, usage tracking, and maintenance alerts into high-end 2-inch pipe threaders. These IoT-enabled tools improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and support predictive maintenance—trends that are gaining traction in industrial and commercial settings. -
Focus on Ergonomics and Safety
As workplace safety regulations tighten, manufacturers are redesigning 2-inch threaders for better ergonomics, reduced vibration, and enhanced grip. Lightweight materials and modular components are being introduced to decrease operator fatigue and injury risk, making these tools more appealing to professional users. -
Growth in Rental and Shared Equipment Models
Equipment rental platforms are expanding, especially in North America and Europe. Small contractors and DIY users are increasingly opting to rent rather than purchase high-cost 2-inch threaders. This trend is influencing manufacturers to design durable, serviceable models suitable for frequent rental use. -
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental regulations are pushing manufacturers to develop energy-efficient motors and use recyclable materials in production. Electric-powered threaders are gaining preference over gas-powered alternatives, aligning with broader industry sustainability goals. -
Competitive Landscape and Regional Shifts
North America remains a dominant market due to stringent building codes and aging infrastructure renewal. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the highest growth rate, led by China, India, and Southeast Asian countries investing in industrial and commercial construction.
In conclusion, the 2-inch pipe threader market in 2026 will be characterized by innovation, digitization, and responsiveness to global infrastructure needs. Companies that invest in smart, efficient, and user-friendly designs will be best positioned to capture market share in this evolving landscape.

Common Pitfalls When Sourcing 2” Pipe Threaders (Quality & IP)
Sourcing a 2-inch pipe threader—especially one that meets high-quality standards and appropriate Ingress Protection (IP) ratings—can present several challenges. Avoiding these common pitfalls ensures reliability, safety, and long-term performance in demanding environments.
Overlooking Build Quality and Material Durability
Many buyers focus solely on price or brand recognition, neglecting the actual construction quality. Low-cost threaders may use inferior steel alloys or plastic components in critical areas, leading to premature wear, stripped gears, or frame deformation under heavy use. Always verify the materials used in the chuck, gearbox, and motor housing—industrial-grade cast iron or reinforced steel is preferable for durability.
Assuming All 2” Threaders Handle True 2” Pipes
Not all tools labeled as “2-inch” can effectively thread pipes at the full 2-inch nominal diameter. Some models may struggle with larger diameters due to insufficient motor power, inadequate die head capacity, or poor torque delivery. Confirm the tool’s specifications explicitly state it supports threading up to 2” NPT (National Pipe Taper) and review performance reviews from users working with large-diameter pipes.
Ignoring IP Rating Requirements for the Work Environment
Ingress Protection (IP) ratings are often overlooked, especially when sourcing for wet, dusty, or outdoor environments. A threader with a low IP rating (e.g., IP20) may fail quickly when exposed to moisture or debris. For outdoor or industrial sites, aim for a minimum of IP54 (dust-protected and splash-resistant) or higher (e.g., IP65 for dust-tight and water-jet resistance). Verify the IP rating applies to the motor and electrical components, not just the casing.
Skipping Die Quality and Compatibility Checks
The threading dies are critical to achieving clean, leak-free threads. Poor-quality dies wear out fast and produce inconsistent threads. Ensure the threader uses hardened, replaceable dies compatible with 2” NPT standards. Also, confirm availability and cost of replacement dies—proprietary or hard-to-find dies increase long-term ownership costs.
Underestimating Power and Torque Needs
Threading 2” steel pipe requires substantial torque. Corded models may lack sufficient power if undersized (e.g., below 1,500 watts), while cordless versions may deplete batteries quickly or stall under load. Assess the motor’s torque output and duty cycle, especially for continuous use. Portable threaders with variable speed and high-torque gear settings are preferable for larger diameters.
Failing to Verify Safety and Certification Standards
In industrial applications, compliance with safety standards (e.g., CE, UL, CSA) is essential. Unverified or non-certified threaders may pose electrical or mechanical hazards. Always request documentation confirming compliance with regional safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations.
Neglecting Service and Support Availability
Even high-quality tools require maintenance. Sourcing from suppliers or brands without accessible technical support, spare parts, or service centers can lead to extended downtime. Prioritize manufacturers with a strong service network and readily available technical documentation.
By addressing these pitfalls proactively, buyers can secure a 2” pipe threader that delivers consistent performance, withstands tough conditions, and offers a reliable return on investment.

Logistics & Compliance Guide for 2 Pipe Threader
Product Overview and Specifications
The 2” Pipe Threader is a heavy-duty industrial tool designed for cutting standard NPT (National Pipe Taper) threads on steel, black iron, and other metal pipes up to 2 inches in diameter. Typically powered by electricity or hydraulic systems, this equipment is commonly used in plumbing, HVAC, and industrial construction settings. Key specifications include motor power (typically 1–2 HP), threading capacity (1/8″ to 2″), and weight (ranging from 30–60 lbs depending on model). Always consult the manufacturer’s manual for exact specifications.
Packaging and Handling Requirements
Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transit. The 2” Pipe Threader should be shipped in a sturdy, corrugated cardboard or wooden crate with internal foam or molded plastic supports to immobilize the unit. All moving parts, including the die head and chuck, must be secured or locked in place. Handles and power cords should be neatly wrapped and fastened. For international shipments, use ISPM 15-compliant wooden packaging if applicable. Label the package with “Fragile,” “This Side Up,” and “Heavy Equipment” indicators.
Transportation and Shipping Guidelines
Transport the 2” Pipe Threader via freight carriers experienced in handling industrial tools. For domestic shipments, LTL (Less-Than-Truckload) freight is recommended for single units, while FTL (Full Truckload) may be used for bulk orders. Secure the unit on a pallet using straps or shrink wrap. Ensure that temperature and humidity remain within safe limits (typically 32°F to 120°F and <85% RH) during transit to protect electrical components. For air freight, verify weight and dimensional restrictions with the carrier. Always provide proper shipping documentation, including a commercial invoice and packing list.
Import/Export Compliance
When shipping internationally, ensure compliance with relevant trade regulations. For export from the U.S., classify the pipe threader under the correct Harmonized System (HS) code—typically 8461.40.00 (machines for threading or tapping). Obtain an ECCN (Export Control Classification Number); most standard pipe threaders fall under EAR99, meaning they are not subject to stringent export controls. However, verify with the manufacturer. For import, comply with destination country regulations—this may require conformity assessment, certification (e.g., CE in the EU, CCC in China), and payment of duties and taxes. Maintain accurate records for at least five years.
Safety and Regulatory Standards
The 2” Pipe Threader must comply with applicable safety standards in the destination market. In the U.S., adherence to OSHA 29 CFR 1910.212 (machine guarding) and ANSI B1.20.1 (pipe thread standards) is required. Electrical models should meet UL 60745 or CSA C22.2 No. 60745 for hand-held motor-operated tools. In the European Union, the CE marking is mandatory under the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC) and Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU). Provide required documentation such as a Declaration of Conformity and user manuals in the local language.
Environmental and Disposal Considerations
The pipe threader contains metal components and potentially hazardous electrical parts. Follow local, state, and federal regulations for disposal. Do not dispose of in regular trash. In the U.S., consult EPA guidelines; in the EU, comply with WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive 2012/19/EU, which mandates proper recycling of electronic tools. Used cutting oils or lubricants should be handled as hazardous waste per RCRA regulations. Encourage end-users to return equipment through certified e-waste recyclers.
Required Documentation and Labeling
Ensure all units are accompanied by essential documentation: user manual, safety instructions, warranty information, and compliance certificates (e.g., UL listing, CE Declaration). Labels on the device must include: manufacturer name, model number, voltage/frequency, serial number, and safety warnings in the local language. For commercial shipments, include a bill of lading, commercial invoice, packing list, and certificate of origin if claiming preferential tariff treatment under trade agreements like USMCA.
Maintenance and User Compliance
End-users must perform regular maintenance as outlined in the manufacturer’s guide to ensure safe and compliant operation. This includes inspecting dies for wear, lubricating moving parts, and checking electrical cords for damage. Only trained personnel should operate the threader. Employers must provide appropriate PPE (gloves, eye protection, hearing protection) and ensure machines are grounded and used in accordance with OSHA or local workplace safety regulations. Record maintenance and training activities for audit purposes.
Conclusion for Sourcing Two Pipe Threaders
After a thorough evaluation of technical requirements, supplier capabilities, cost considerations, and long-term operational needs, sourcing two pipe threaders is a justified and strategic decision. The selected models meet the required specifications for durability, efficiency, and compatibility with existing tools and workflows. Supplier comparisons revealed competitive pricing, reliable after-sales support, and warranty terms that ensure minimal downtime and maintenance costs.
Acquiring two units allows for increased productivity by enabling simultaneous work on multiple job sites or supporting team operations without equipment bottlenecks. Additionally, having a backup unit improves operational continuity and reduces risks associated with equipment failure.
In conclusion, the procurement of two pipe threaders represents a cost-effective investment that enhances operational efficiency, supports project scalability, and aligns with organizational goals for reliability and performance in field operations.