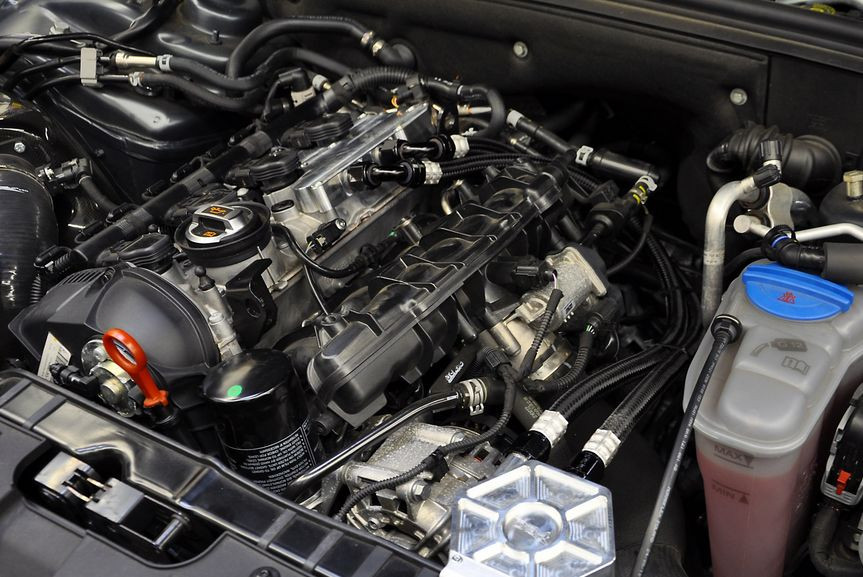
The global turbocharged engine market, particularly for the 1.8L displacement segment, continues to gain momentum due to increasing demand for fuel-efficient powertrains that maintain strong performance. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global turbocharger market was valued at USD 23.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 6.8% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is largely driven by stringent emissions regulations and automakers’ shift toward downsized, turbocharged engines—of which the 1.8-liter turbo variant remains a popular choice in compact and midsize vehicles. Advancements in direct fuel injection, variable valve timing, and turbo technology have enhanced reliability and output, making this engine size a staple across major manufacturers. With production spread across North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific, the 1.8 turbo engine has become a benchmark for efficiency and performance in modern gasoline powertrains. Here are the top seven manufacturers leading innovation and volume in this segment.
Top 7 1.8 Turbo Engine Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 VW/Audi 1.8T Parts & Accessories
Domain Est. 2001
Website: ecstuning.com
Key Highlights: Find VW/Audi 1.8T Parts from our Top Brands. Keep your Volkswagen running like new with 1.8T parts and accessories from the best OEM and aftermarket suppliers ……
#2 VW/Audi 1.8 20V Turbo swaps in to Mk3 MR2
Domain Est. 2016
Website: stavtech.co.uk
Key Highlights: The loom is a hybrid of a factory 1.8T and MR2 engine loom, and is almost completely plug-in, with just a few wires left to connect which are supplied fully ……
#3 Volkswagen’s latest turbocharged TSI engine debuts in the Jetta and …
Domain Est. 1994
Website: media.vw.com
Key Highlights: New 1.8-liter EA888 Gen 3 turbocharged and direct-injection engine replaces 2.5-liter five cylinder, offering more torque, refinement, performance, and better ……
#4 The Audi 1.8 TFSI
Domain Est. 1996
Website: press.audi.co.uk
Key Highlights: The optimised turbocharger and a new engine management system bring a further improvement in responsiveness and help the torque to build up even more smoothly….
#5 VW Audi 1.8 Turbo Engine
Domain Est. 2008
Website: rwdmotorsport.com
Key Highlights: A four-cylinder engine with three inlet and two exhaust valves driven off two camshafts, the VAG 1.8 20V turbo first appeared in 150PS form in the Audi A6 then ……
#6 1.8T Race Engines – Car Racing Feeling
Domain Est. 2022
Website: bar-tek.com
Key Highlights: 30-day returnsDrive stably and reliably over 300 PS: Completely tuned 1.8T race engines for Audi and VW. More performance, torque and driving pleasure are preprogrammed….
#7 Replacement engine 1.8T 20V BFB 1.8 Turbo Engine overhaul repair
Website: mikmotoren.de
Key Highlights: In stock 1–9 day deliveryThe BFB engine offered here for the price of €2990.00 has been professionally overhauled and has also been improved. Our engine repair service in the ……
Expert Sourcing Insights for 1.8 Turbo Engine
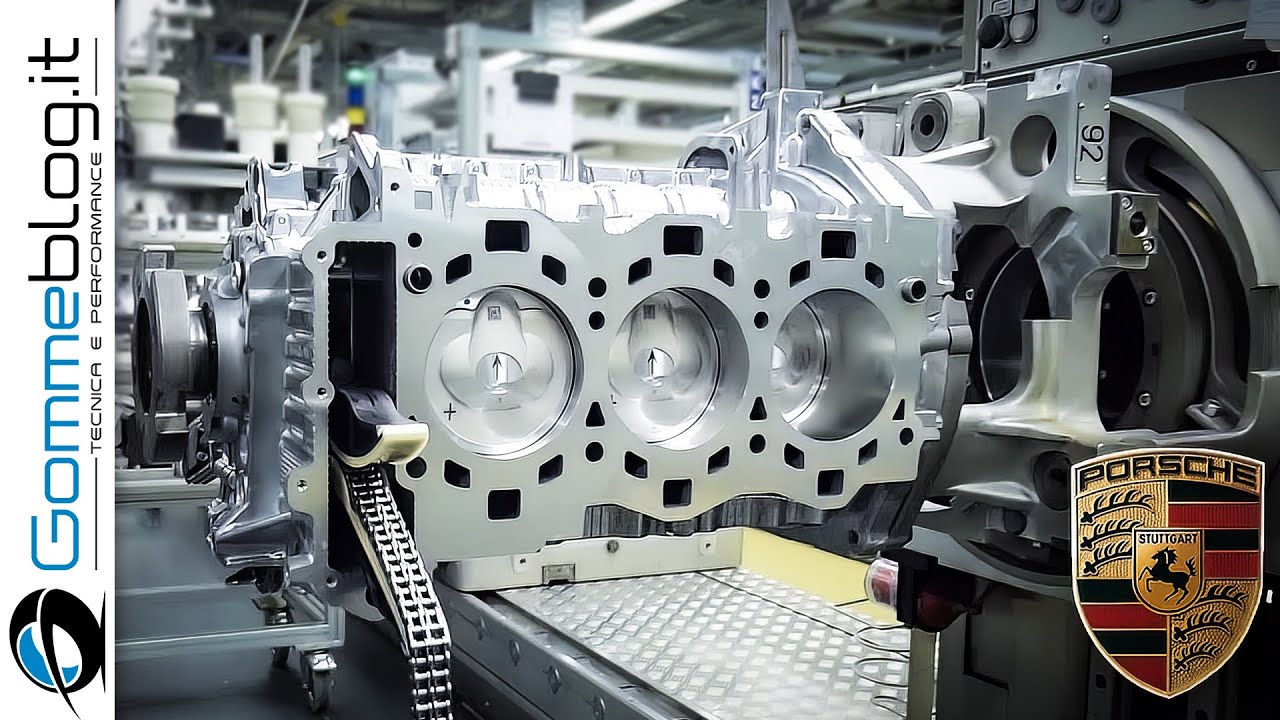
H2: 2026 Market Trends for 1.8L Turbo Engine
As the automotive industry evolves toward electrification and stricter emissions regulations, the 1.8L turbocharged gasoline engine is expected to occupy a transitional but increasingly niche position in the 2026 market landscape. While not the dominant powertrain of the future, the 1.8L turbo engine will retain relevance in specific segments due to its balance of performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Key trends influencing its market position in 2026 include:
1. Decline in New Vehicle Adoption
By 2026, automakers are accelerating their shift toward electrified powertrains. As a result, the inclusion of 1.8L turbo engines in new vehicle platforms—especially in Europe and China—is expected to decline. Brands are phasing out internal combustion engines (ICEs) in favor of hybrids and full electric vehicles (EVs) to meet regulatory targets. However, in emerging markets and certain mid-tier vehicle segments, the 1.8L turbo will persist due to lower production costs and consumer demand for affordable performance.
2. Strong Aftermarket and Replacement Demand
Despite reduced OEM integration, the 1.8L turbo engine will maintain robust aftermarket demand. Millions of vehicles currently on the road—particularly models from manufacturers like Volkswagen, Toyota, Honda, and Ford—utilize variants of this engine. As these vehicles age, replacement engines, turbochargers, and related components will drive significant aftermarket activity in 2026.
3. Hybridization and Mild Hybrid Integration
Some manufacturers may extend the life of the 1.8L turbo by integrating it into mild hybrid systems (e.g., 48V architectures). This approach enhances fuel efficiency and reduces emissions without requiring a complete powertrain overhaul. For example, certain SUVs and CUVs may continue to use the 1.8L turbo as part of a hybrid setup, particularly in regions where EV infrastructure is underdeveloped.
4. Regional Market Divergence
In North America and parts of Asia (notably India and Southeast Asia), the 1.8L turbo will retain stronger appeal due to consumer preference for affordable turbocharged performance and slower EV adoption rates. In contrast, Western Europe and China will see minimal new deployment of this engine type, favoring plug-in hybrids and battery electric vehicles instead.
5. Focus on Efficiency and Emissions Optimization
Manufacturers still producing 1.8L turbo engines will prioritize advanced technologies such as high-pressure direct injection, variable valve timing, and improved turbo response to meet tightening emissions standards (e.g., Euro 7, China 6b). These enhancements will help maintain compliance while preserving drivability.
6. Competition from Smaller and Alternative Engines
The 1.8L turbo faces increasing competition from smaller turbocharged engines (e.g., 1.5L) and alternative fuels (e.g., CNG, biofuels). Downsizing trends and efficiency gains in smaller displacements may reduce the 1.8L’s appeal in compact and midsize vehicles.
Conclusion
In 2026, the 1.8L turbo engine will no longer be at the forefront of new automotive innovation but will remain a relevant powertrain option in specific contexts—particularly in the aftermarket, emerging markets, and hybrid configurations. Its future lies not in growth, but in adaptation and sustained support for existing vehicle fleets.
Common Pitfalls When Sourcing a 1.8 Turbo Engine (Quality and Intellectual Property)
Sourcing a 1.8 Turbo engine—whether for replacement, restoration, or integration into a new application—can present several challenges, particularly in terms of quality assurance and intellectual property (IP) risks. Being aware of these pitfalls helps prevent costly mistakes, legal complications, and performance issues.
1. Quality-Related Pitfalls
a. Inconsistent Manufacturing Standards
Engines sourced from third-party or non-OEM suppliers may not adhere to the original manufacturer’s specifications. Variations in materials, machining tolerances, or assembly processes can lead to:
– Reduced reliability and lifespan
– Poor fuel efficiency
– Increased emissions
– Compatibility issues with existing vehicle systems
b. Remanufactured or Refurbished Engines of Unknown Origin
Many suppliers offer “reconditioned” 1.8 Turbo engines. However, there is often a lack of transparency regarding:
– The engine’s service history
– Which components were replaced or repaired
– Whether proper testing (e.g., compression tests, leak-down tests) was conducted
Without certification or warranty, buyers risk acquiring an engine with hidden defects.
c. Counterfeit or Substandard Components
Low-cost engines from certain regions may use counterfeit or inferior parts (e.g., pistons, turbochargers, gaskets). These components:
– Fail prematurely under stress
– May not meet safety or environmental standards
– Void warranties on associated vehicle systems
d. Lack of Compatibility Verification
Even if the engine is genuine, variations in:
– Engine control unit (ECU) programming
– Mounting configurations
– Ancillary attachments (alternator, A/C compressor)
can cause integration issues, especially across model years or regional variants.
2. Intellectual Property (IP) Risks
a. Unauthorized Reproduction or Knock-offs
Some manufacturers in unregulated markets produce unauthorized replicas of OEM 1.8 Turbo engines (e.g., mimicking VW EA888, Ford EcoBoost, or GM turbocharged units). These may infringe on:
– Patents for engine design and turbocharging systems
– Trademarks associated with branding and logos
– Copyrighted software in embedded ECUs
Using such engines can expose buyers or integrators to legal liability, especially in commercial applications.
b. Use of Proprietary Software Without Licensing
Modern turbocharged engines rely on proprietary engine management software. Sourcing engines with cloned or hacked ECUs:
– Violates software copyrights
– May trigger diagnostic errors or malfunctions
– Prevents future updates and servicing through official channels
c. Grey Market Imports and IP Infringement
Engines imported through grey markets may:
– Bypass regional IP protections
– Lack proper licensing for local use
– Include components restricted by international trade agreements
This poses risks for both importers and end-users, especially in regulated industries.
d. Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Without proper documentation (e.g., certificates of authenticity, bill of materials), it’s difficult to verify whether an engine or its components:
– Were legally produced
– Respect original IP rights
– Can be legally registered or insured
Mitigation Strategies
- Source from Authorized Distributors or OEMs: Ensures compliance with quality and IP standards.
- Request Detailed Documentation: Ask for service history, test results, and compliance certifications.
- Verify Software Authenticity: Ensure ECUs and firmware are original and properly licensed.
- Conduct Third-Party Inspections: Use independent mechanics or labs to assess engine condition and authenticity.
- Consult Legal Advisors: When sourcing in bulk or for commercial use, ensure compliance with IP and import regulations.
By proactively addressing these quality and IP concerns, stakeholders can avoid performance failures, legal exposure, and reputational damage when sourcing a 1.8 Turbo engine.

H2: Logistics & Compliance Guide for 1.8L Turbo Engine
This guide outlines the essential logistics and compliance considerations for the handling, transportation, import/export, and regulatory adherence of the 1.8L Turbo Engine throughout the supply chain.
H3: Regulatory Compliance
Emissions & Environmental Regulations
– EPA Certification (USA): Ensure engine meets current Tier 3 or equivalent EPA emission standards. Verify Certificate of Conformity (CoC) is issued and valid.
– Euro Standards (EU/UK): Confirm compliance with Euro 6d or latest applicable standard. Required E-marking and EU type-approval documentation must accompany shipments.
– China VI (CN): For Chinese market, compliance with China VI (b) standards is mandatory. Local certification via CCC (China Compulsory Certification) required.
– Noise Regulations: Engine must meet regional noise emission limits (e.g., UN ECE R51 for EU).
Safety & Certification
– DOT/SAE Standards (USA): Compliance with relevant SAE J and FMVSS standards for engine systems.
– UN R83 (Global): Required for engines intended for use in vehicles subject to international vehicle regulations.
– REACH & RoHS (EU): Ensure restricted substances (e.g., lead, mercury, certain phthalates) are below thresholds. Maintain full material declarations (FMD).
H3: Packaging & Handling
Packaging Requirements
– Use moisture-resistant, vibration-dampened packaging with anti-corrosion protection (e.g., VCI paper or coating).
– Secure engine on wooden or composite pallets with bracing to prevent movement.
– Seal in vacuum or dry-air-filled plastic wrap to prevent internal condensation during transit.
– Include desiccant packs and humidity indicators inside packaging.
Labeling
– Clearly label with:
– Engine model and serial number
– Gross/Net weight
– “Fragile” and “This Side Up” indicators
– Hazard symbols if applicable (e.g., oil residue)
– Country of origin
– Barcodes/QR codes for traceability
H3: Transportation & Logistics
Mode of Transport
– Ocean Freight: Use ISO containers with dunnage and moisture control. Monitor humidity during long-haul shipments.
– Air Freight: Preferred for urgent deliveries; ensure packaging meets IATA dangerous goods regulations (if fluids present).
– Overland (Truck/Rail): Use enclosed, climate-controlled trailers where possible. Secure load with straps and edge protectors.
Storage Conditions
– Store in dry, temperature-controlled environment (5°C to 35°C recommended).
– Limit exposure to direct sunlight and corrosive atmospheres.
– Rotate stock using FIFO (First In, First Out) inventory practice.
H3: Import/Export Documentation
Required Documents
– Commercial Invoice (with HS Code: 8407.31 or 8407.32 for spark-ignition engines)
– Packing List
– Bill of Lading/Air Waybill
– Certificate of Origin
– EPA/EC Type Approval Certificates
– REACH/RoHS Compliance Declaration
– Import License (if required by destination country)
Customs Clearance
– Verify HS code classification accuracy to avoid delays or incorrect tariffs.
– Coordinate with licensed customs brokers in destination country.
– Prepare for potential customs inspections; ensure engines are easily accessible.
H3: Aftermarket & Field Compliance
Recall & Service Bulletin Management
– Maintain traceability via engine serial numbers.
– Comply with regional recall notification requirements (e.g., NHTSA in USA).
– Distribute service updates in accordance with local regulatory mandates.
End-of-Life (ELV) Compliance
– Adhere to EU End-of-Life Vehicles Directive (2000/53/EC) or equivalent.
– Provide de-pollution instructions and material recovery guidelines.
H3: Audit & Record Retention
- Maintain compliance records (certifications, test reports, shipping logs) for minimum of 10 years.
- Conduct annual internal audits of logistics and compliance procedures.
- Prepare for unannounced regulatory inspections by authorities.
Note: Regulations vary by country and are subject to change. Always consult local legal and compliance experts before shipment.
In conclusion, sourcing a 1.8L turbo engine requires careful consideration of compatibility, condition, provenance, and cost-effectiveness. Whether intended for a repair, restoration, or performance upgrade, it is essential to verify the engine’s specifications—such as model year, emissions standards, power output, and integration with existing vehicle systems. Reputable sources including OEM dealers, verified used engine suppliers, and trusted online marketplaces can provide reliable options, while thorough inspection or warranties help mitigate risks. Additionally, factoring in installation costs, tuning requirements, and long-term reliability ensures a successful outcome. With due diligence and proper planning, sourcing a 1.8L turbo engine can deliver a powerful, efficient, and dependable solution for your automotive needs.