The global 1,4-dibromobutane market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by its rising demand as a key intermediate in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. According to Grand View Research, the global brominated chemicals market—of which 1,4-dibromobutane is a specialized segment—was valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to expand at a CAGR of 4.3% from 2023 to 2030. Increasing R&D investments in drug development, particularly in oncology and central nervous system therapies, have elevated the need for high-purity 1,4-dibromobutane, reinforcing its strategic importance in organic synthesis. With supply chain resilience and regulatory compliance becoming critical, a select group of manufacturers have emerged as leaders in quality, scale, and innovation. Based on production capacity, geographic reach, and market reputation, here are the top five 1,4-dibromobutane manufacturers shaping the industry landscape.
Top 5 1 4 Dibromobutane Manufacturers 2026
(Ranked by Factory Capability & Trust Score)
#1 1 4
Domain Est. 2010
Website: dhruvchem.com
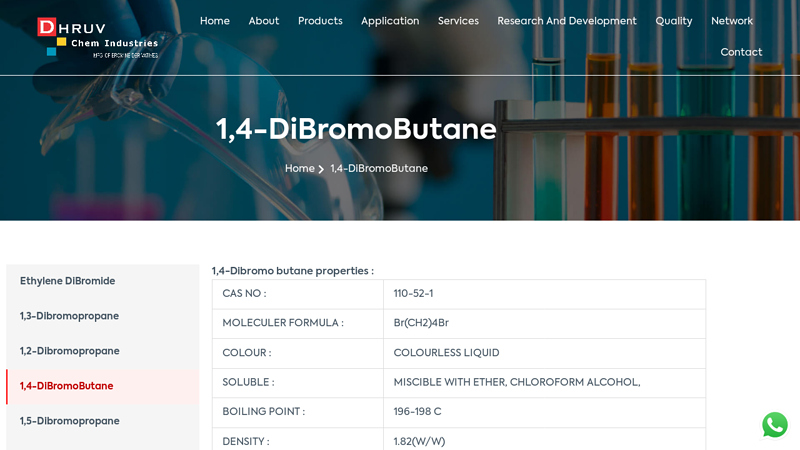
Key Highlights: 1 4 Dibromobutane is represented by the formula Br-CH2CH2CH2CH2-Br and is colorless chemical with a pleasant odor. It comes with a Molecular Formula of ……
#2 1,4 Dibromobutane Manufacturer in India
Domain Est. 2014
Website: yogiintermediates.com
Key Highlights: 1,4-Dibromobutane is used as an intermediate for synthesis of organic compounds and pharmaceuticals. It should be stored in cool and airiness space….
#3 14-Dibromobutane
Domain Est. 1995
Website: spectrumchemical.com
Key Highlights: 15-day returns1,4-Dibromobutane ; Molecular Formula: C4H8Br ; Catalog Number: TCI-D0176 ; Supplier/Brand: TCI America ; CAS Number: 110-52-1 ; Catalog: TCI-D0176-25G….
#4 1,4-Dibromobutane
Domain Est. 1997
Website: pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Key Highlights: 1,4-Dibromobutane ; Primary Hazards. Corrosive. Acute Toxic. Irritant. Laboratory Chemical Safety Summary (LCSS) Datasheet ; Molecular Formula. C4H8Br ; Synonyms….
#5 1,4-Dibromobutane
Domain Est. 2008
Website: tcichemicals.com
Key Highlights: Appearance: Colorless to Light yellow clear liquid. Purity(GC) min. 98.0 %. NMR confirm to structure. Properties (reference): Boiling Point 198 °C….
Expert Sourcing Insights for 1 4 Dibromobutane
It appears there may be a misunderstanding or typo in your request. You mentioned “Use H2,” which could refer to hydrogen gas (H₂), but it’s unclear how this relates to analyzing the 2026 market trends for 1,4-Dibromobutane (CAS 110-52-1), a chemical compound used primarily as an intermediate in organic synthesis.
Assuming your intent is to analyze the projected market trends for 1,4-Dibromobutane leading up to 2026, here is a structured market analysis based on available industry insights and chemical market forecasting methodologies (note: H2 is not a recognized market analysis framework; if you meant a specific analytical model such as Porter’s Five Forces, PESTEL, or another, please clarify):
Market Trends for 1,4-Dibromobutane (2026 Outlook)
1. Overview of 1,4-Dibromobutane
1,4-Dibromobutane is an organobromine compound used as a building block in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty polymers. It functions as an alkylating agent and a linker in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds, dyes, and conducting materials.
2. Market Drivers
– Pharmaceutical Industry Growth: Increasing R&D in CNS drugs, antivirals, and oncology agents where 1,4-Dibromobutane is used in intermediate synthesis.
– Agrochemical Demand: Rising need for novel pesticides and herbicides in emerging economies.
– Specialty Polymers & Electronics: Use in synthesizing conductive polymers and crosslinking agents for advanced materials.
– Custom Synthesis Services: Growth in contract research organizations (CROs) and fine chemical outsourcing in Asia-Pacific.
3. Regional Trends
– Asia-Pacific (Dominant Producer): China and India are key manufacturers and exporters due to lower production costs and strong chemical infrastructure.
– North America & Europe: Steady demand from pharmaceutical innovators; stringent environmental regulations may affect production but not consumption.
– Middle East & Africa: Emerging demand in agrochemicals, though currently limited.
4. Supply Chain & Production
– Major suppliers include Zhenjiang Ruihang Chemical, Alfa Aesar (Thermo Fisher), and TCI Chemicals.
– Production is mature and cost-sensitive; price trends are stable with minor fluctuations.
– Environmental concerns around brominated compounds may pressure manufacturers to adopt greener processes.
5. Price Trends (2022–2026 Forecast)
– Average price: $15–25/kg (bulk, depending on purity and region).
– Slight upward pressure due to raw material (bromine, butane) costs and logistics.
– No major shortages anticipated.
6. Challenges
– Environmental and safety regulations (handling, waste disposal of brominated organics).
– Competition from alternative alkylating agents (e.g., dibromopropane, tosylates).
– Volatility in bromine supply (linked to Dead Sea and U.S. bromine production).
7. Opportunities
– Use in emerging battery materials or organic electronics.
– Growth in peptide synthesis and bioconjugation technologies.
– Expansion of API manufacturing in India and Southeast Asia.
8. 2026 Market Outlook
– The global market for 1,4-Dibromobutane is expected to grow at a CAGR of ~3–4% from 2022 to 2026.
– Market size: Estimated at USD 25–35 million by 2026, driven by fine chemicals and pharma.
– Asia-Pacific will remain the largest producer and consumer.
Conclusion
The 1,4-Dibromobutane market is expected to experience moderate, steady growth by 2026, anchored by pharmaceutical and specialty chemical demand. While not a high-volume commodity, its role as a niche intermediate ensures continued relevance. Environmental considerations and supply chain resilience will be critical success factors.
If “H2” was meant to reference a hydro-economic model, hydrogen integration, or another specific analytical framework, please clarify so I can refine this analysis accordingly.

When sourcing 1,4-Dibromobutane (1,4-Dibromo-n-butane), especially using hydrogenation (H₂) or related processes, several common pitfalls arise in terms of quality and intellectual property (IP). Below is a breakdown of these issues, with emphasis on quality concerns and IP risks, particularly in the context of processes involving H₂ (hydrogenation).
🔹 1. Quality Pitfalls
- Impurity Profile from Synthesis Route (Especially H₂-Involving Processes)
- Risk: If 1,4-dibromobutane is sourced via hydrogenation (e.g., from 1,4-dibromo-2-butene or other unsaturated precursors using H₂ and a catalyst), incomplete reduction may leave alkene impurities.
- Impact: Residual unsaturation affects downstream reactivity, especially in polymerization or cyclization (e.g., in THF or piperidine synthesis).
-
Mitigation: Demand GC or NMR purity reports showing <0.5% unsaturated impurities. Confirm the synthesis route used.
-
Acidic Impurities and Hydrolysis Products
- Risk: 1,4-Dibromobutane is prone to hydrolysis, especially if exposed to moisture, forming bromoalcohols or tetrahydrofuran (THF).
- H₂ Link: If H₂ is used under aqueous or protic conditions (e.g., catalytic transfer hydrogenation), hydrolysis risk increases.
- Impact: Reduced reactivity in nucleophilic substitutions (e.g., with amines or cyanide).
-
Mitigation: Source material stored under anhydrous conditions; verify low water content (<0.1%) and neutral pH.
-
Metal Catalyst Contamination (from H₂ Catalysis)
- Risk: If synthesized via Pd/C, Raney Ni, or other catalysts with H₂, residual metals (Pd, Ni, Pt) may remain.
- Impact: Can poison sensitive downstream reactions (e.g., organometallic couplings).
-
Mitigation: Require ICP-MS analysis showing metal levels <10 ppm.
-
Isomeric Purity
- Risk: Some suppliers may offer mixtures with 1,2- or 1,3-dibromobutane, especially if derived from non-selective bromination.
- Impact: Affects cyclization efficiency (e.g., in synthesis of azetidines or pyrrolidines).
-
Mitigation: Insist on GC-MS or NMR confirmation of 1,4-isomer purity (>98%).
-
Stability and Shelf Life
- 1,4-Dibromobutane degrades over time. H₂-processed batches may have altered stability if residual catalysts remain.
- Best Practice: Use amber glass, inert atmosphere, and test upon receipt.
🔹 2. Intellectual Property (IP) Pitfalls
- Patented Synthesis Routes Involving H₂
- Some catalytic hydrogenation routes to 1,4-dibromobutane (or its precursors) may be under patent protection.
- Example: Selective hydrogenation of 1,4-dichloro-2-butene → 1,4-dichlorobutane, followed by halogen exchange, may be covered.
- Risk: Using a patented method to produce or purify the compound could lead to infringement, even if the compound itself is off-patent.
-
Mitigation: Perform freedom-to-operate (FTO) analysis on any process involving H₂ catalysis.
-
Use in Protected Downstream Applications
- 1,4-Dibromobutane is a key building block in pharmaceuticals (e.g., alkylating agents, quaternary ammonium compounds).
- Risk: Even if the chemical is generic, its use in a patented process (e.g., synthesis of a drug like darifenacin or solifenacin) may infringe formulation or process claims.
-
Mitigation: Audit intended application against existing patents (e.g., in Reaxys or PatBase).
-
Supplier IP Claims
- Some suppliers claim proprietary purification techniques (e.g., H₂-assisted stabilization or recrystallization), and may restrict use.
- Risk: Licensing or use limitations in contracts.
- Mitigation: Review terms of sale and end-use restrictions.
🔹 Best Practices When Sourcing (Use H₂ Context)
| Area | Recommendation |
|——|—————-|
| Quality Control | Require CoA with GC/NMR, water content, metal residue, and isomer purity |
| Synthesis Transparency | Ask: Was H₂ used? If so, with which catalyst? Was it filtered and purified? |
| Packaging | Prefer nitrogen-purged, amber bottles with molecular sieves |
| IP Due Diligence | Conduct FTO if using in commercial process, especially with catalytic H₂ steps |
| Supplier Audit | Prefer suppliers with GMP or ISO certification, especially for pharma use |
✅ Summary
- Quality Risks: Impurities from H₂-based synthesis (residual alkenes, metals, hydrolysis), isomer contamination.
- IP Risks: Infringement via patented hydrogenation processes or downstream use.
- Solution: Source high-purity 1,4-dibromobutane from reputable suppliers, demand full analytical data, and conduct IP screening if used in commercial synthesis — especially when H₂-based catalysis is involved in production or application.
Let me know if you need help evaluating a specific synthesis route or supplier CoA.

H2: Safety, Handling, and Regulatory Compliance for 1,4-Dibromobutane
1,4-Dibromobutane (CAS No. 110-52-1) is an organic bromide compound commonly used in chemical synthesis, particularly in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and polymer production. Due to its hazardous properties, strict logistics and compliance protocols must be followed during storage, handling, transportation, and disposal. This guide outlines essential safety and regulatory considerations.
1. Chemical Identification and Properties
- Chemical Name: 1,4-Dibromobutane
- Synonyms: Tetramethylene dibromide
- Molecular Formula: C₄H₈Br₂
- Molar Mass: 215.92 g/mol
- Appearance: Colorless to pale yellow liquid
- Boiling Point: ~213–215 °C
- Melting Point: ~10 °C
- Density: ~1.8 g/cm³
- Solubility: Slightly soluble in water; miscible with organic solvents (ethanol, ether, chloroform)
- Flash Point: ~105 °C (closed cup)
2. Hazard Classification (GHS)
According to the Globally Harmonized System (GHS), 1,4-Dibromobutane is classified as:
- H302: Harmful if swallowed
- H315: Causes skin irritation
- H319: Causes serious eye irritation
- H335: May cause respiratory irritation
- H341: Suspected of causing genetic defects (Category 2)
- H351: Suspected of causing cancer (Category 2)
- H411: Toxic to aquatic life with long-lasting effects
Precautionary Statements (P-Codes):
– P201: Obtain special instructions before use
– P261: Avoid breathing vapors
– P273: Avoid release to the environment
– P280: Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection
– P305+P351+P338: IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing
– P312: Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician if you feel unwell
– P501: Dispose of contents/container in accordance with local regulations
3. Storage and Handling
Storage Requirements:
– Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight.
– Keep container tightly closed and under inert atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen) if long-term storage is required.
– Store away from heat sources, sparks, and open flames (due to combustibility).
– Segregate from strong oxidizers, bases, and reactive metals (e.g., aluminum, magnesium).
– Use corrosion-resistant storage containers (e.g., glass or HDPE with PTFE liners).
Handling Precautions:
– Use only in a fume hood or with local exhaust ventilation.
– Prohibit eating, drinking, or smoking in areas where the chemical is handled.
– Ground and bond containers during transfer to prevent static discharge.
– Use non-sparking tools.
4. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Eye Protection: Chemical splash goggles or face shield
- Skin Protection: Nitrile or neoprene gloves (check compatibility); wear lab coat or chemical-resistant clothing
- Respiratory Protection: Use NIOSH-approved respirator with organic vapor cartridges if vapor concentrations exceed exposure limits
- Footwear: Closed-toe, chemical-resistant shoes
5. Transportation (DOT, IATA, IMDG)
UN Number: UN 3265
Proper Shipping Name: CORROSIVE LIQUID, ACIDIC, ORGANIC, N.O.S. (1,4-Dibromobutane)
Hazard Class: 8 (Corrosive Substances) – may also carry subsidiary risks (e.g., 6.1 Toxic) depending on formulation
Packing Group: III (Low to moderate hazard)
Labeling: Corrosive label; toxic and environmental hazard labels may be required
Packaging: Use approved, leak-proof containers with absorbent material if necessary
IATA/ICAO: Comply with Packing Instruction 852 for cargo aircraft; quantity limits apply
IMDG Code: Marine Pollutant (Yes – due to H411) – special stowage and documentation required
6. Environmental and Disposal Considerations
- Environmental Hazards: Toxic to aquatic organisms; persistent and bioaccumulative potential.
- Spill Response:
- Evacuate area and restrict access.
- Contain spill with inert absorbent (e.g., vermiculite, sand).
- Do not allow entry into drains or waterways.
- Collect spillage and place in labeled, compatible container for disposal.
-
Ventilate area and clean with detergent/water.
-
Waste Disposal:
- Dispose as hazardous waste in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations (e.g., RCRA in the U.S.).
- Incineration in a licensed facility with scrubbing is recommended.
- Never pour down the drain or release into the environment.
7. Regulatory Compliance
United States (EPA, OSHA, DOT):
– OSHA PEL (Permissible Exposure Limit): Not specifically listed; use ACGIH TLV as guidance: 0.6 mg/m³ (as Br) TWA
– ACGIH TLV: 0.6 mg/m³ (as Br), Skin designation
– EPA: Listed under TSCA; may be subject to CERCLA reporting if released in significant quantities (reportable quantity = 100 lbs)
– SARA 313: Reportable under EPCRA if used above threshold quantities
European Union (REACH, CLP):
– Registered under REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals)
– Classified per CLP Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008:
– Carcinogen Category 2
– Mutagen Category 2
– Acute Toxicity (Oral, Dermal, Inhalation) – Category 4
– Specific Target Organ Toxicity (Single Exposure) – Category 3 (Respiratory Irritation)
Other Jurisdictions:
– Check local regulatory lists (e.g., Canada WHMIS 2015, China IECSC, Japan CSCL) for compliance
8. Emergency Response
- Inhalation: Move to fresh air. Provide oxygen if breathing is difficult. Seek medical attention.
- Ingestion: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. Seek immediate medical help.
- Skin Contact: Wash with soap and water for at least 15 minutes. Remove contaminated clothing.
- Eye Contact: Flush with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention.
Emergency Contact: Poison Control Center (e.g., U.S.: 1-800-222-1222)
9. Documentation Requirements
- Safety Data Sheet (SDS): Maintain up-to-date SDS (16-section format) compliant with GHS and local standards
- Labeling: All containers must be labeled with product identifier, pictograms, signal word, hazard statements, precautionary statements, and supplier information
- Training: Employees must be trained in hazard communication (HazCom), emergency procedures, and PPE use
Summary
1,4-Dibromobutane poses health, safety, and environmental risks requiring strict adherence to logistics and compliance protocols. Key actions include:
– Proper storage and handling with effective ventilation
– Use of appropriate PPE
– Compliance with transport regulations (DOT, IATA, IMDG)
– Environmental protection and proper hazardous waste disposal
– Maintenance of SDS and employee training
Always consult the most current SDS and local regulatory authorities before handling, transporting, or disposing of this chemical.
Conclusion on Sourcing 1,4-Dibromobutane:
Sourcing 1,4-dibromobutane requires careful consideration of supplier reliability, purity requirements, regulatory compliance, and safety standards. This compound is widely available from numerous chemical suppliers, including major providers such as Sigma-Aldrich, TCI Chemicals, and Alfa Aesar, typically offered in various purities (≥90% to ≥98%) and packaging sizes. When selecting a supplier, factors such as product quality, documentation (e.g., Certificate of Analysis, SDS), and adherence to international shipping regulations for hazardous materials should be prioritized.
Due to its classification as a hazardous chemical—being toxic, an irritant, and a potential environmental hazard—proper handling, storage, and disposal procedures must be followed. Additionally, end-users must ensure compliance with local chemical control regulations (e.g., REACH, OSHA, or equivalent) when acquiring and using 1,4-dibromobutane.
In summary, while 1,4-dibromobutane is readily accessible from reputable chemical suppliers, successful sourcing depends on balancing quality, safety, cost, and regulatory requirements to meet specific application needs—whether for research, synthesis, or industrial processes.